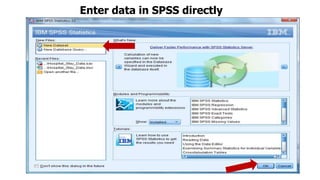
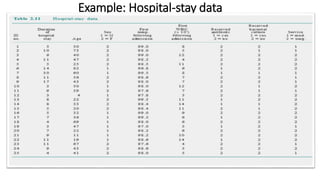
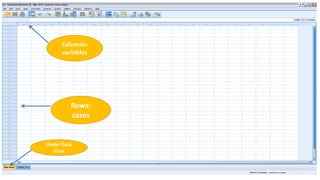
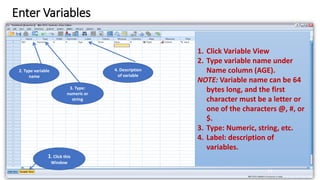
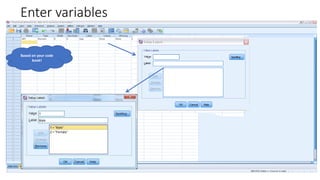
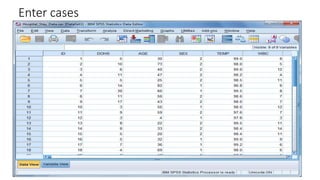
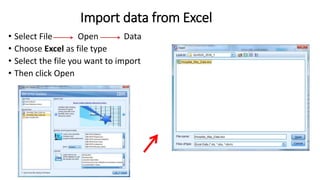
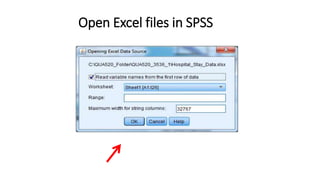
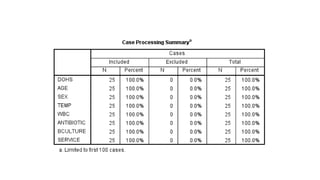
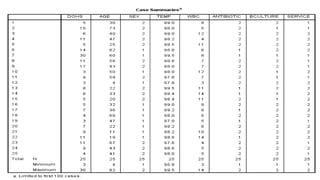
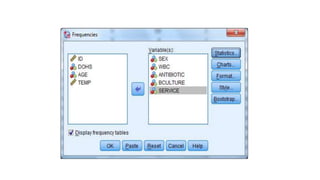
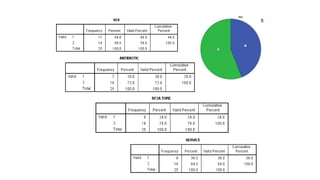
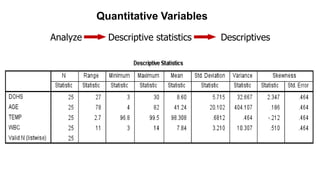
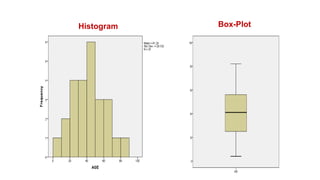
This document provides an introduction to using the SPSS statistical software. It outlines the SPSS interface, including the data and variable views. It describes how to enter data directly into SPSS and import external data files. It also explains how to clean and edit data, define variables, and obtain basic descriptive statistics through functions like frequencies, summaries, and descriptive analysis. The goal is to introduce the user to the key components and functionality of the SPSS interface.