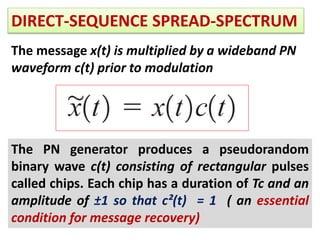
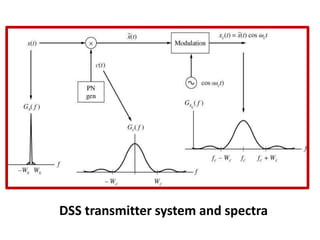
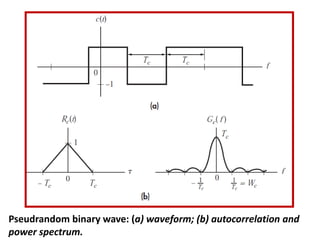
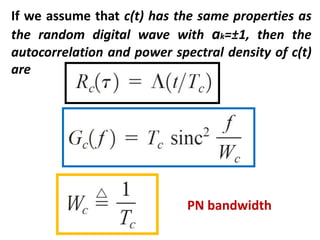
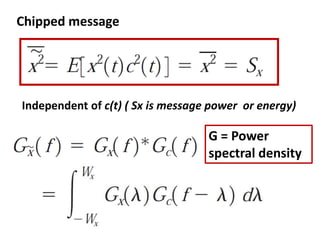
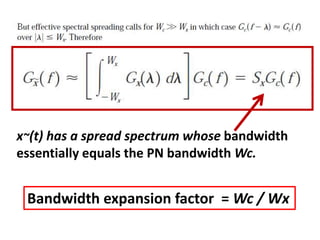
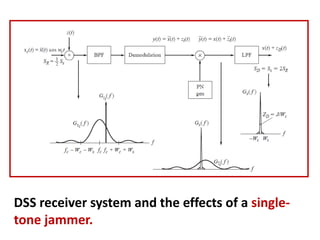
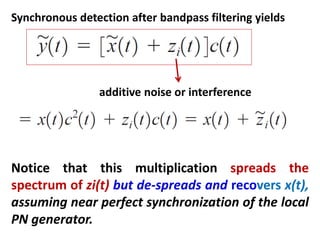
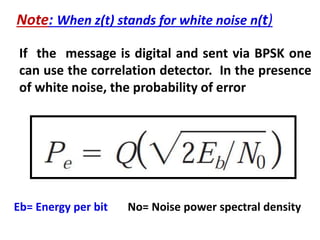
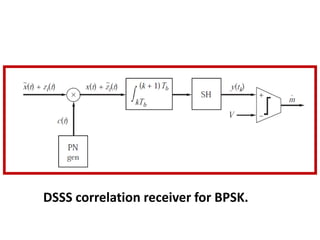
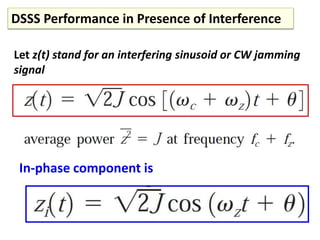
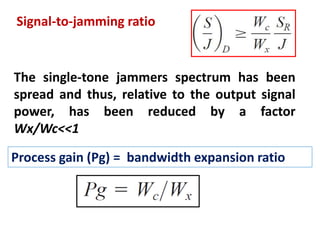
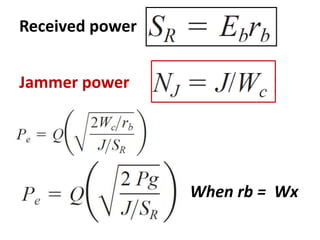
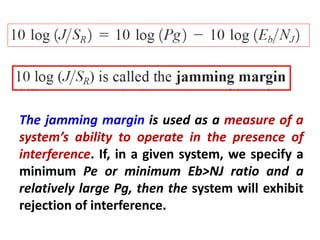
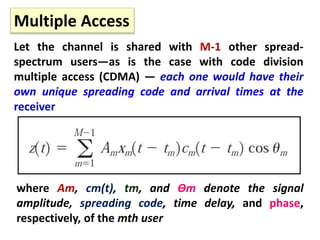
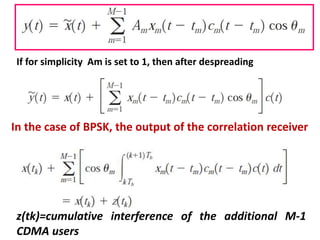
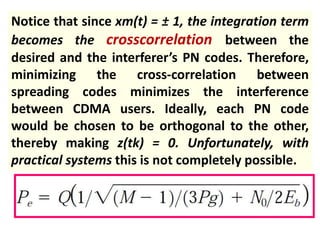
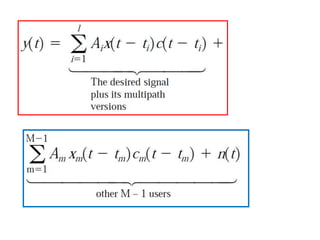
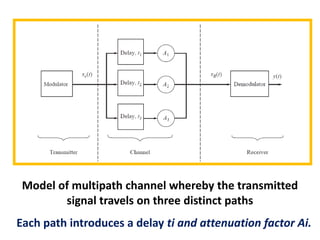
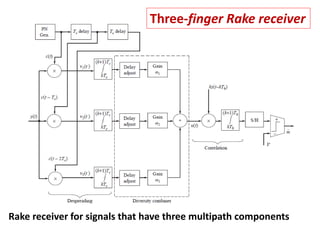
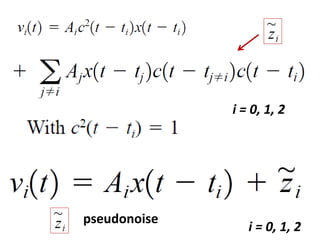
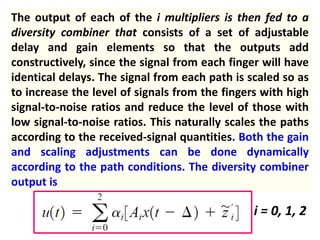
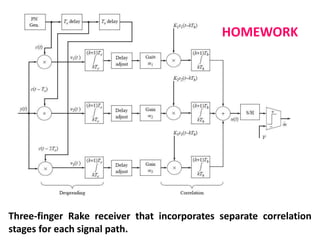
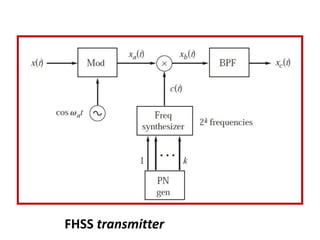
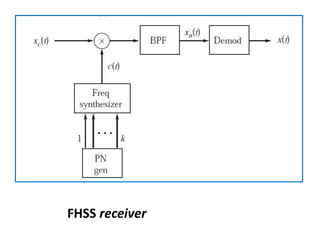
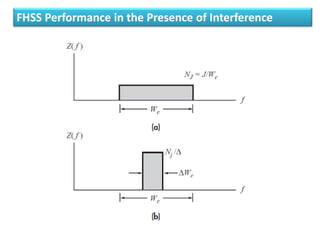
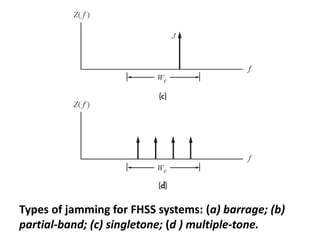
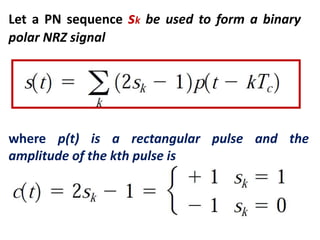
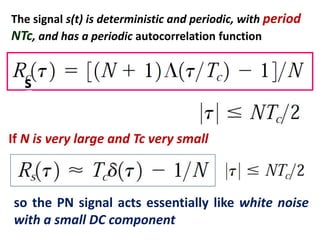
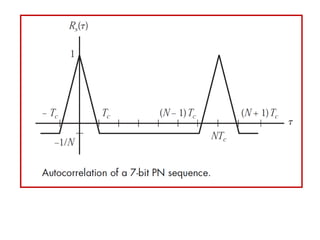
Direct-sequence spread spectrum techniques multiply a message signal by a pseudorandom noise code to spread the signal's bandwidth. At the receiver, synchronization of the local pseudorandom code allows recovery of the original message signal. Frequency-hopping spread spectrum transmits a message signal over multiple carrier frequencies according to a pseudorandom hopping sequence, making jamming or interception more difficult. The document describes the operation of direct-sequence and frequency-hopping transmitters and receivers, and discusses performance in the presence of interference and jamming.










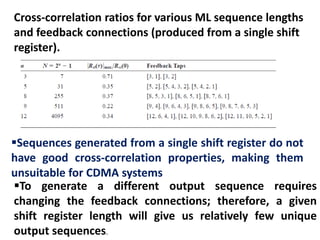
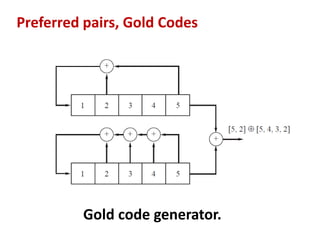
![Shift register sequence generator with [5, 2] configuration
If the appropriate feedback tap connections are
made, then an n-bit register can produce a
maximal-length (ML)
second and fifth
cells are tapped](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spreadspectrum333-161228213035/85/Spread-Spectrum-Techniques-38-320.jpg)

![Example: Autocorrelation of a [3,1] Shift Register
A 3-bit, [3, 1] shift register configuration with values of
111 produces a periodic ML sequence of 1110100 with N
=7.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spreadspectrum333-161228213035/85/Spread-Spectrum-Techniques-42-320.jpg)
![Cross-
correlation
of [3,1] and
[3,2] PN
sequences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spreadspectrum333-161228213035/85/Spread-Spectrum-Techniques-44-320.jpg)
![Auto- and crosscorrelation of [3, 1] and [3, 2] PN
sequences.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spreadspectrum333-161228213035/85/Spread-Spectrum-Techniques-45-320.jpg)