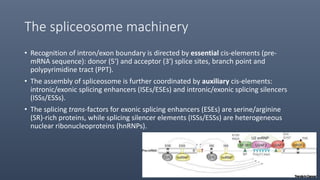
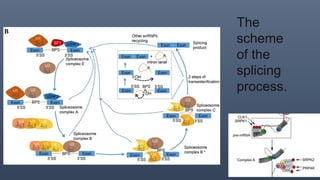
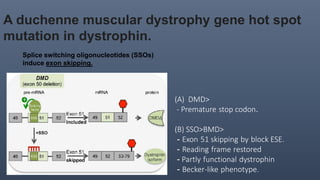
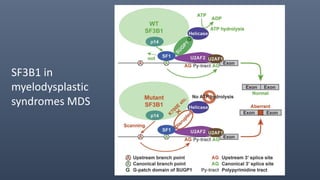
The spliceosome is a large molecular machine that catalyzes pre-mRNA splicing. It is composed of five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) and over 300 proteins. Mutations that affect splicing can cause diseases like Duchenne muscular dystrophy and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In DMD, splice-switching oligonucleotides induce exon skipping to restore the reading frame. In MDS, mutations in splicing factors SF3B1 and U2AF1 promote aberrant splicing and contribute to pathogenesis. Alternative splicing of VEGF pre-mRNA produces pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic isoforms impacting cancer. Detection methods like minigene assays and RT-PCR analyze