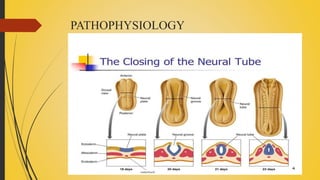
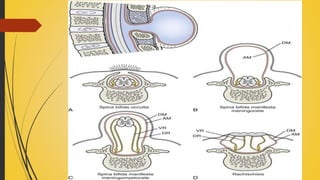
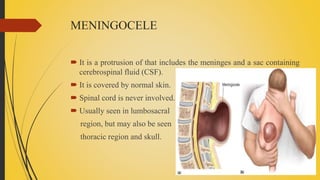
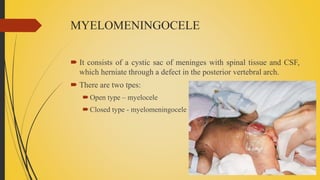
Spina bifida is a birth defect where the spinal cord fails to close properly, leaving it exposed. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, which has no protrusion and is usually asymptomatic; meningocele, which involves protrusion of meninges and cerebrospinal fluid in a sac; and myelomeningocele, the most severe form, which involves protrusion of meninges, spinal cord, and cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment involves surgery to close the defect as well as management of any related conditions like hydrocephalus or paralysis. Parents are counseled and trained to care for the child's lifelong medical needs.