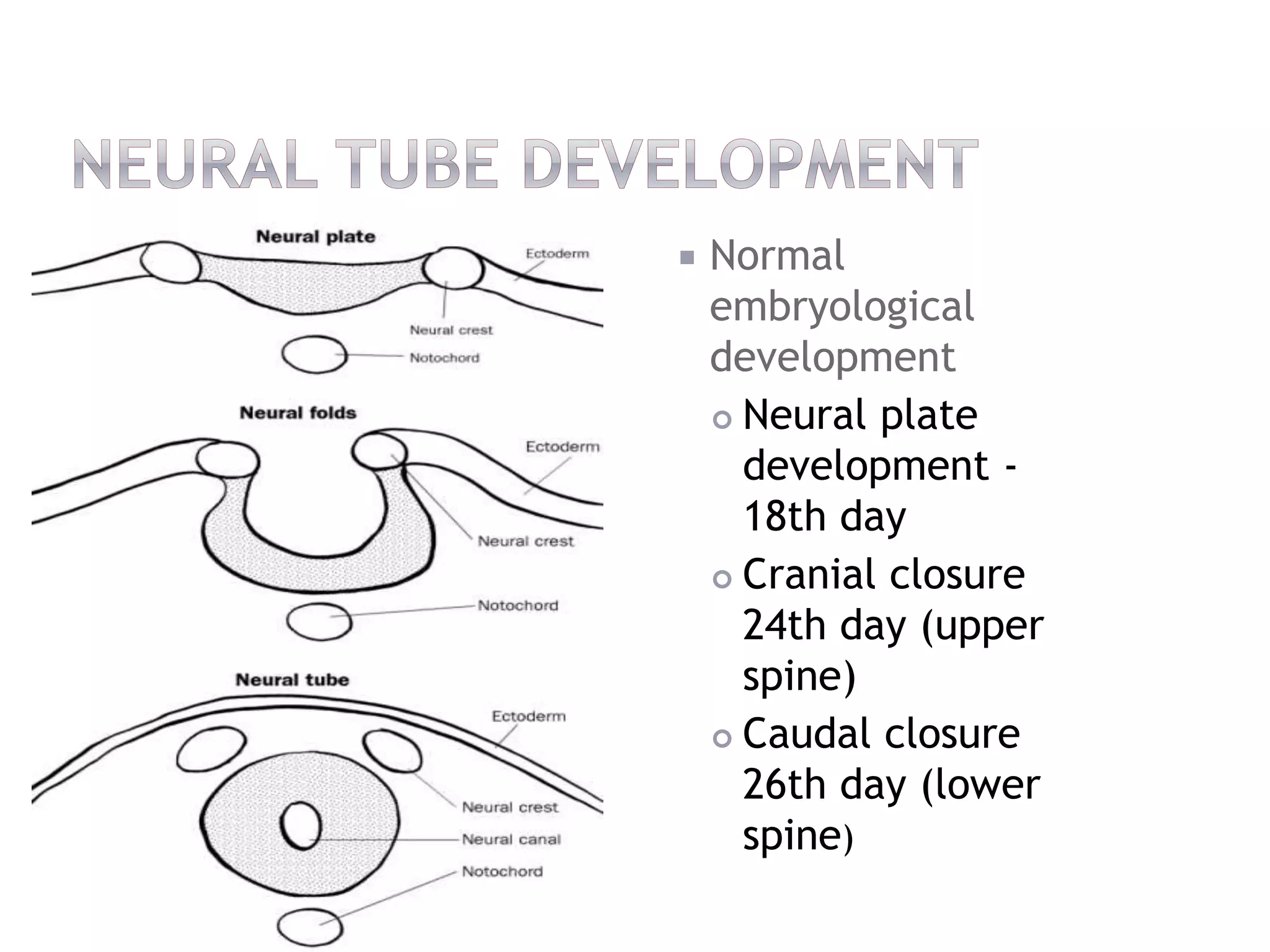
This document discusses neural tube defects (NTDs), including spina bifida, anencephaly, and encephalocele. It describes the normal embryonic development of the neural tube and causes of NTDs, which can include genetic and environmental factors like folic acid deficiency. Management involves prenatal screening, surgical repair after birth, lifelong treatment of symptoms like paralysis, and prevention through folic acid supplementation before and during pregnancy. Children with NTDs may experience permanent disabilities and require ongoing monitoring and support.