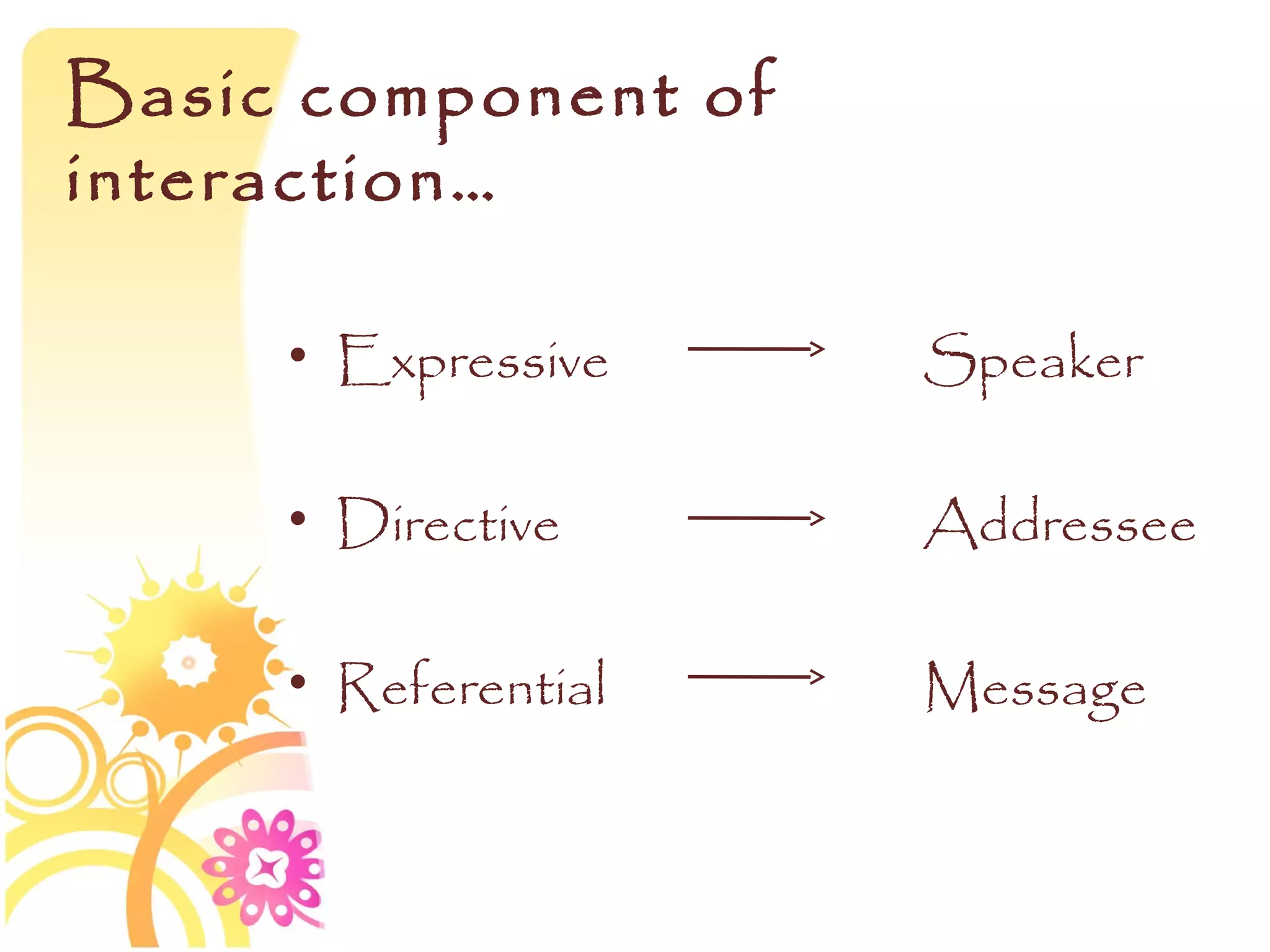
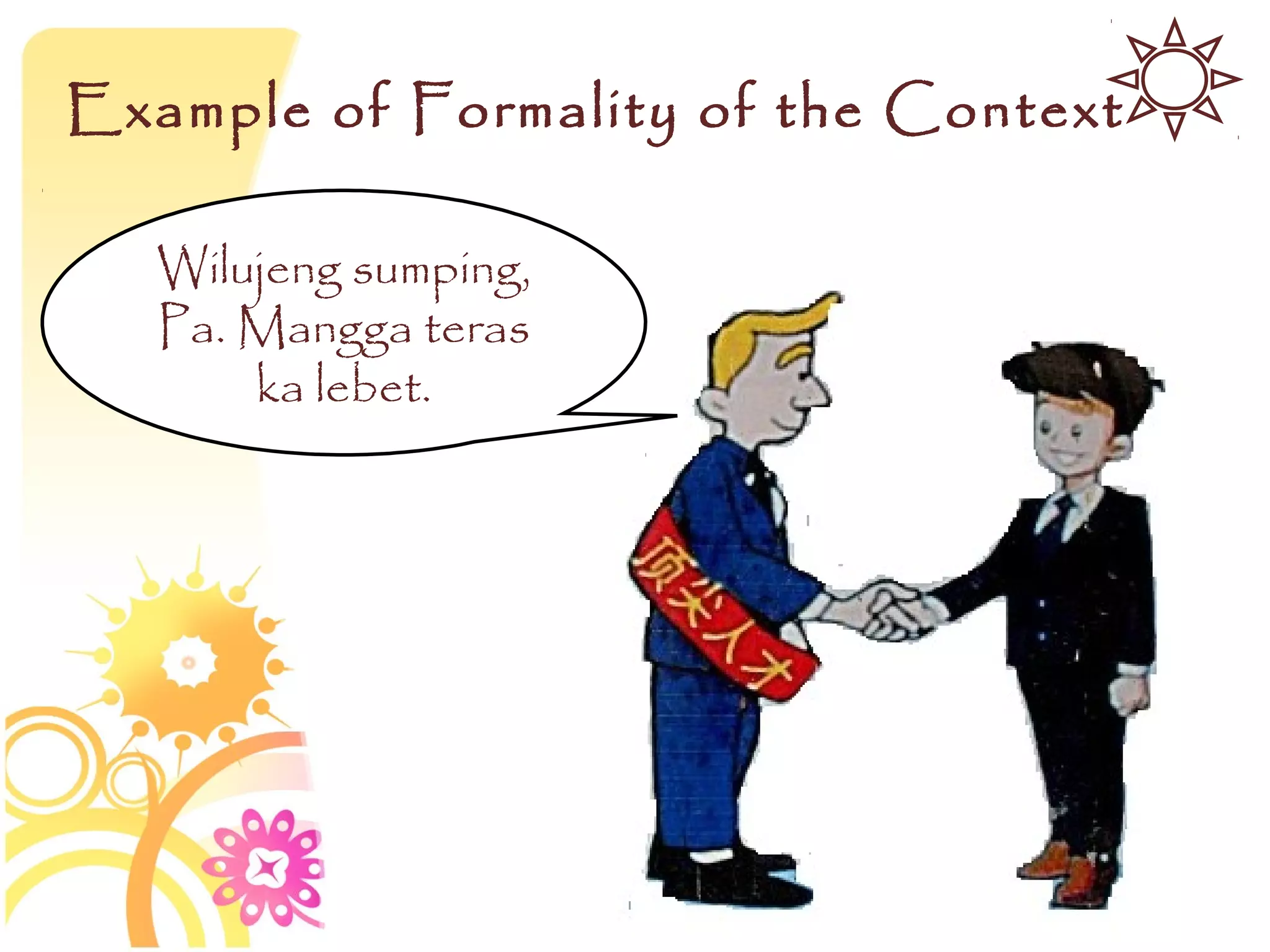
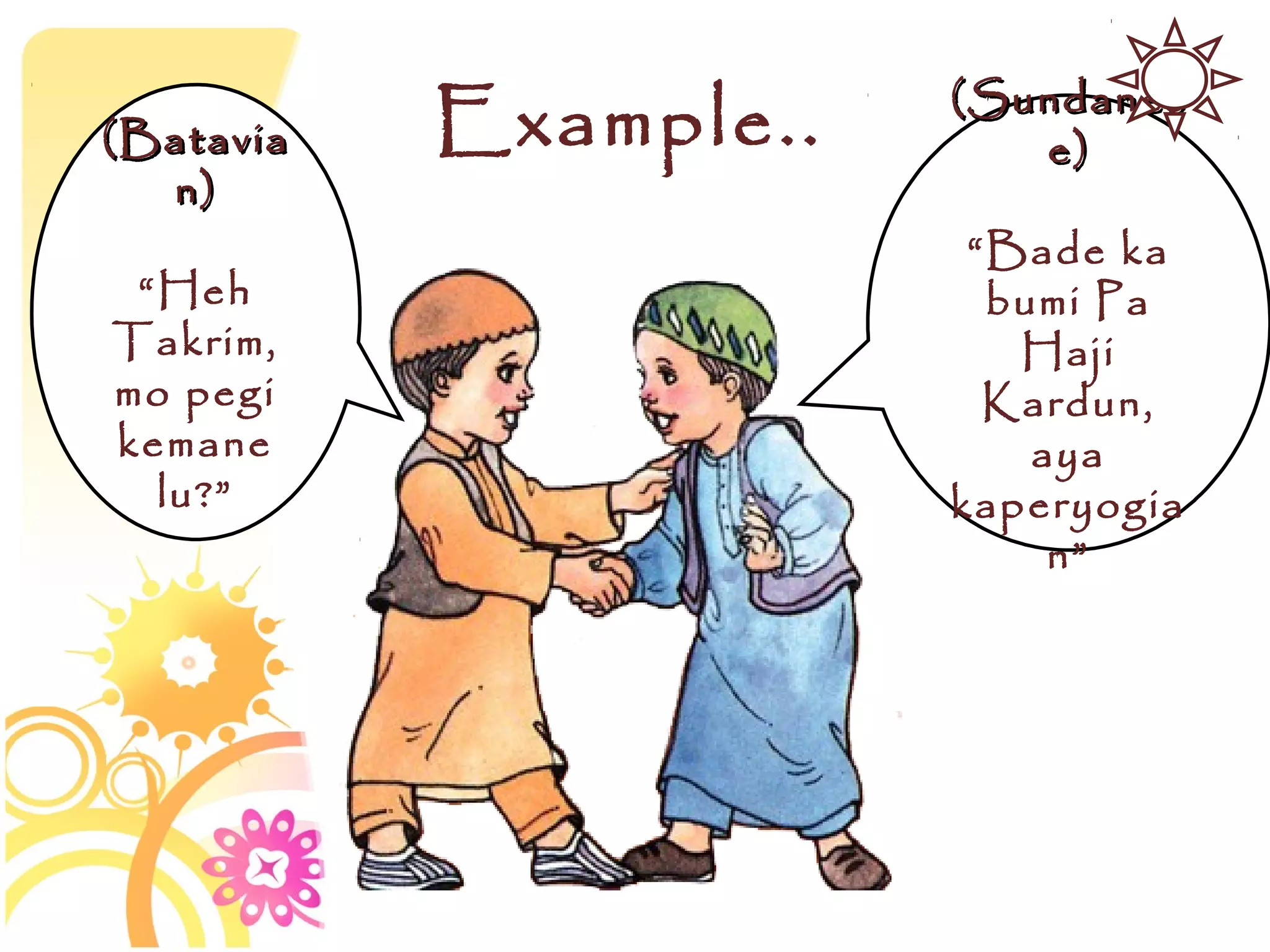
This document discusses speech functions, politeness, and cross-cultural communication. It defines different speech functions such as expressive, directive, referential, metalinguistic, poetic, and phatic utterances. The document also discusses how directives concern getting people to do things and can vary based on social distance, relative status, and formality of context. Politeness also varies across cultures and can be shown through positive and negative politeness as well as different address forms and greetings. Miscommunication may occur between cultures with different assumptions about linguistic politeness.