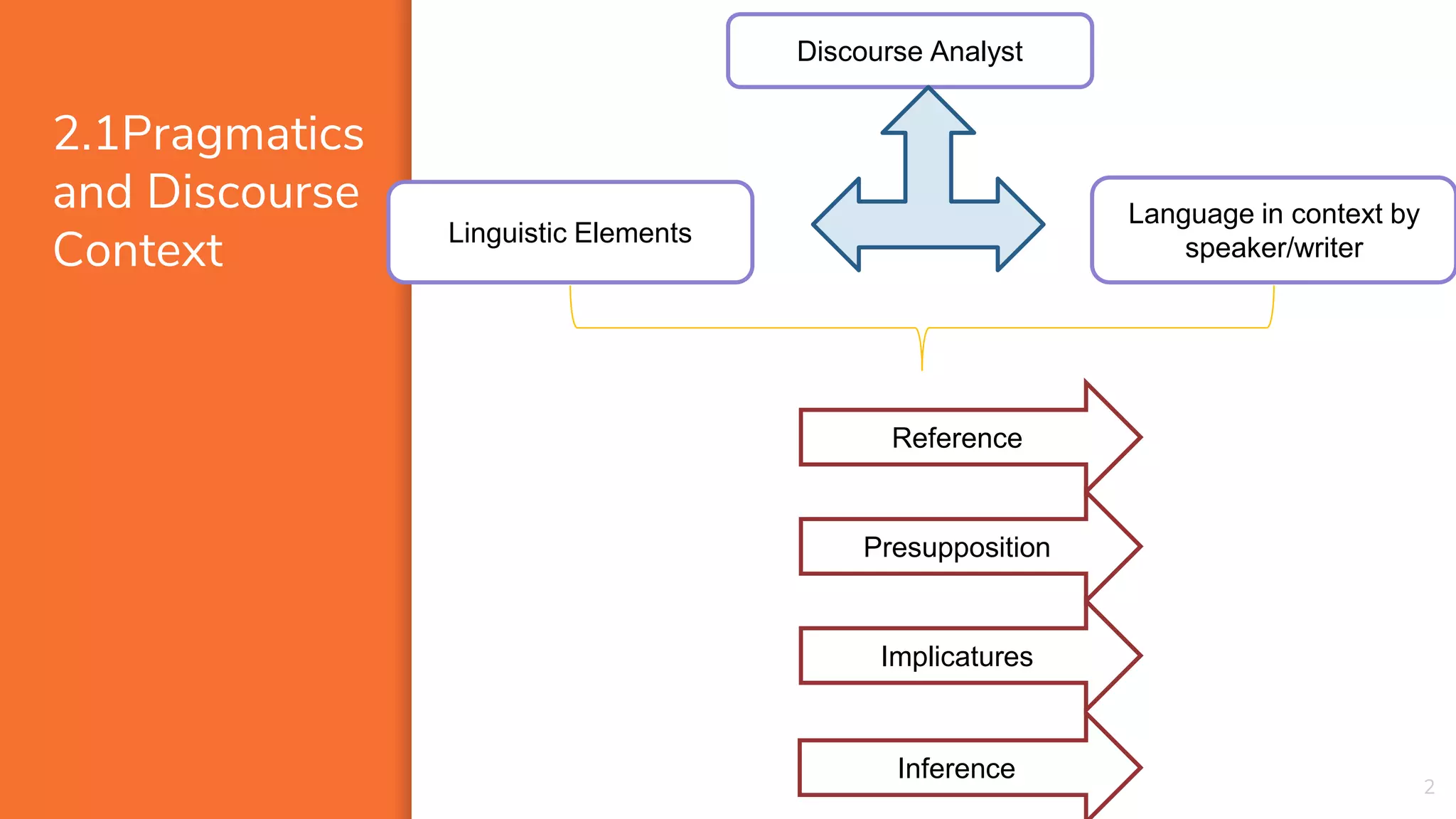
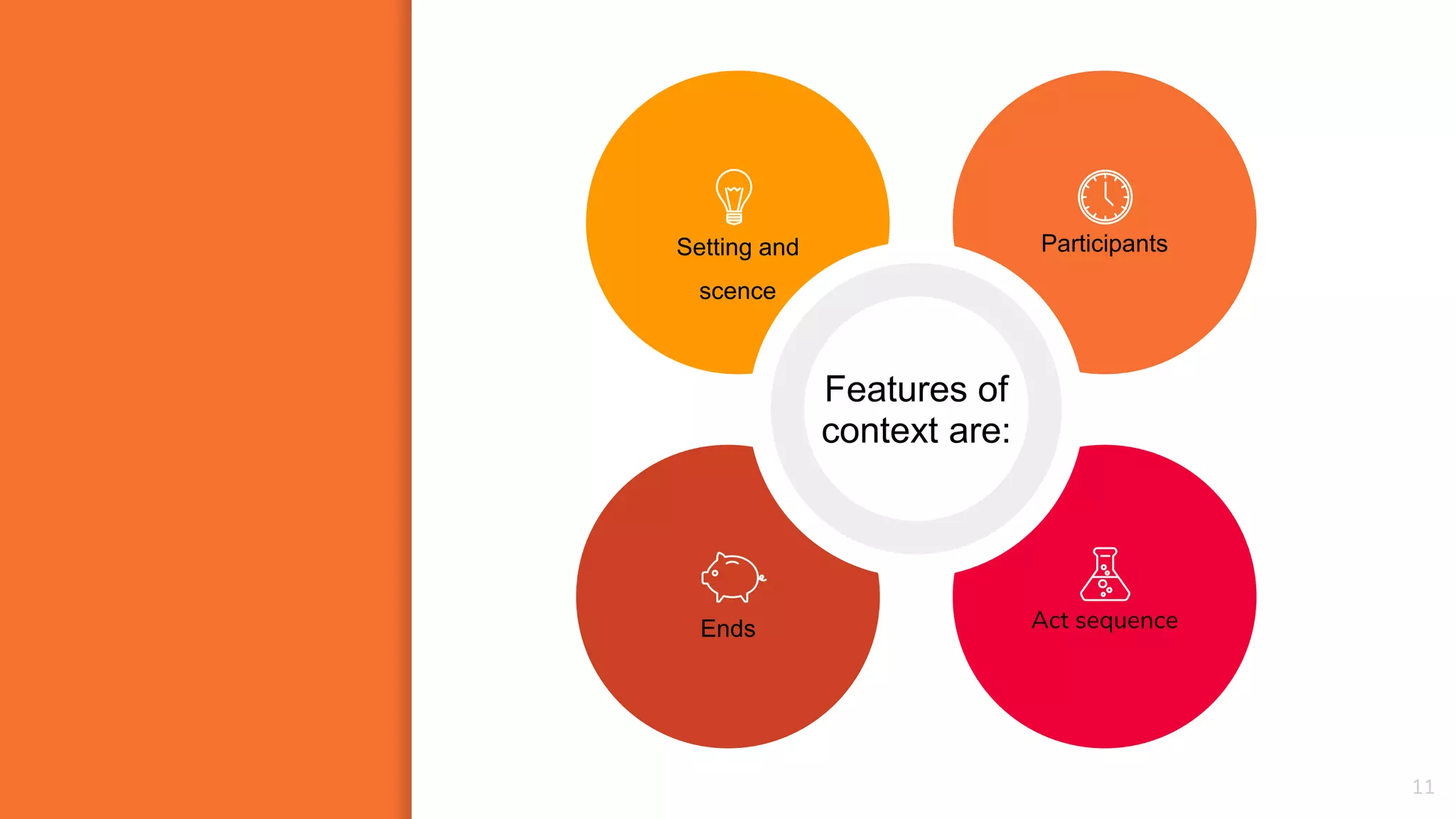
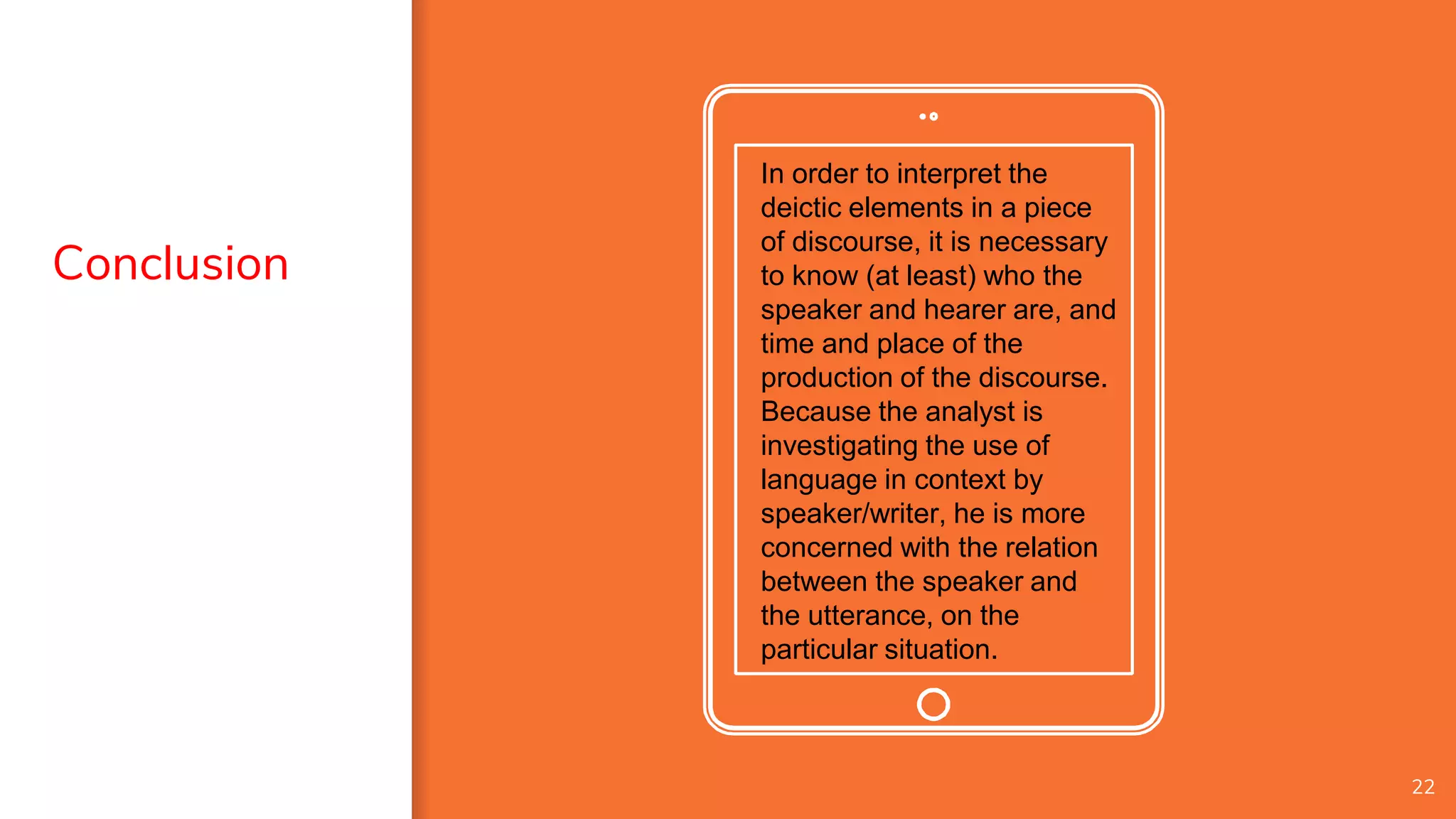
1) Context plays an important role in the interpretation of language. Context includes features like participants, setting, topics being discussed, and previous statements.
2) There are different types of context - physical context surrounding an utterance ("co-text") and broader social context. Interpretation is constrained by context.
3) Analysts must consider principles like local interpretation, where the context used is the minimum needed to understand meaning, and analogy, where new statements are understood based on past similar experiences. Understanding context is essential for interpreting deixis and relationships between speakers, utterances, and situations.