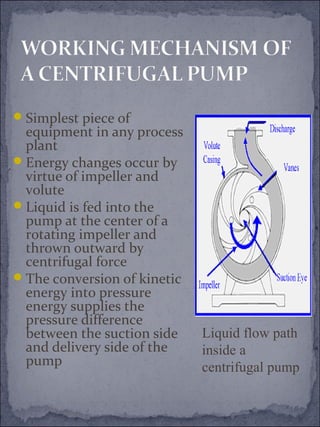
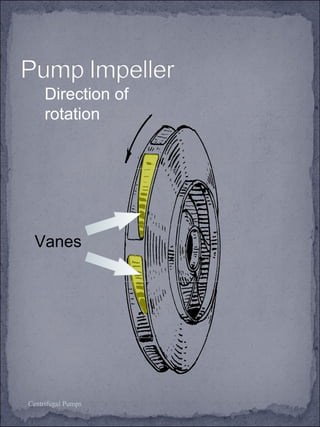
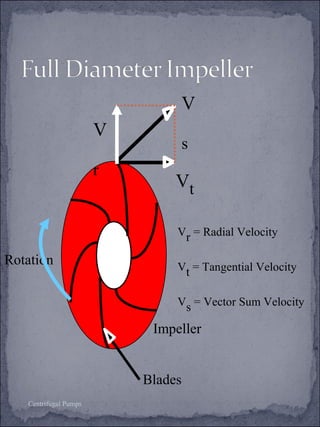
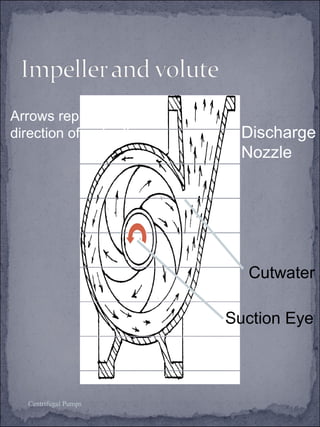
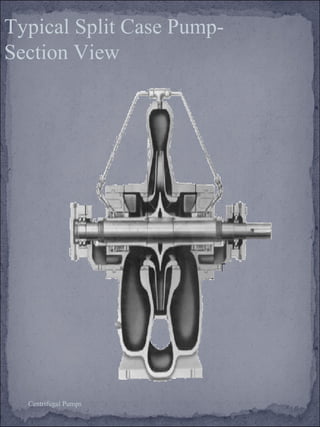
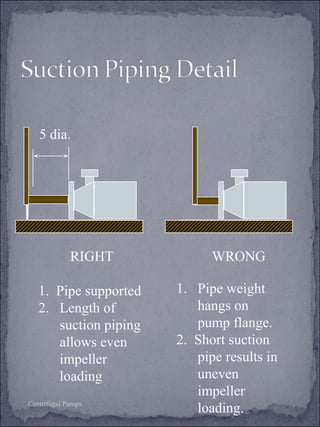
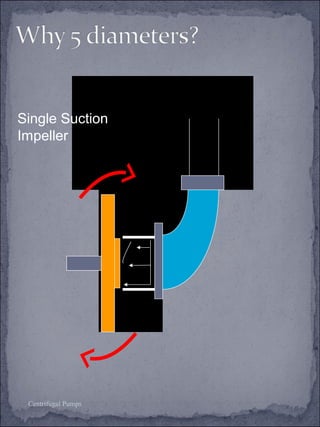
The document discusses centrifugal pumps, including their working mechanism, operation, advantages, and disadvantages. Centrifugal pumps use a rotating impeller to impart centrifugal force on liquid and increase pressure to pump water from a low point to a higher point. They are simple to operate but work best over a narrow range of conditions and cannot handle highly viscous liquids efficiently.