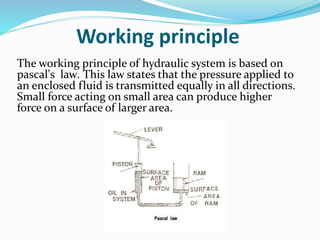
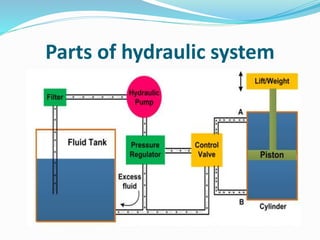
The document discusses hydraulic systems used in mobile applications. It provides an overview of basic hydraulic systems and their advantages like being lighter weight and developing unlimited force. Hydraulic systems are widely used in mobile equipment like tractors, construction vehicles, and aircraft. The case study section examines the hydraulic system used in tractors for lifting and lowering agricultural implements. It describes the key components like the pump, valves, motor, and cylinder and explains how hydraulic pressure is used to transfer force via Pascal's law.