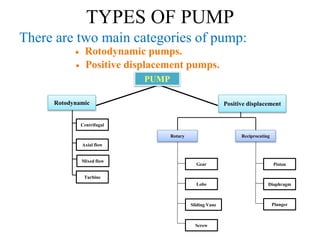
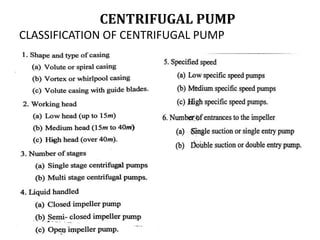
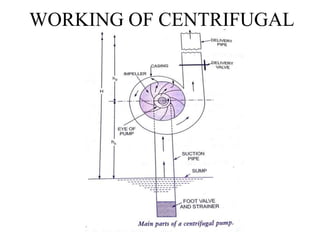
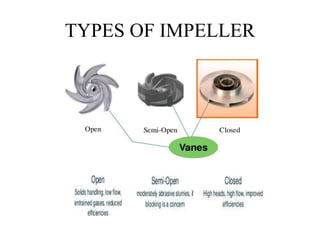
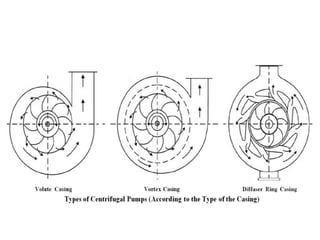
The document discusses centrifugal pumps. It defines a pump as a hydraulic machine that converts mechanical energy to hydraulic energy in the form of pressure. There are two main types of pumps - rotodynamic pumps which use centrifugal force to increase pressure, and positive displacement pumps which displace liquid using moving parts like pistons. Centrifugal pumps specifically work by spinning an impeller to impart centrifugal force on the fluid, pushing it outward and increasing pressure so it can flow to a higher level through the delivery pipe. The main parts of a centrifugal pump are the impeller, casing, suction pipe with foot valve and strainer, and delivery pipe. The impeller spins inside the casing to increase pressure on the fluid, which