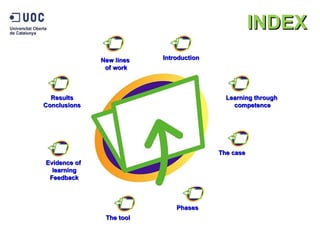
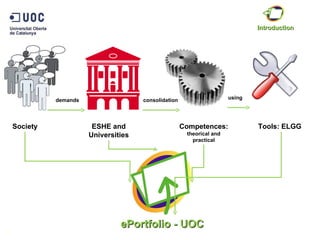
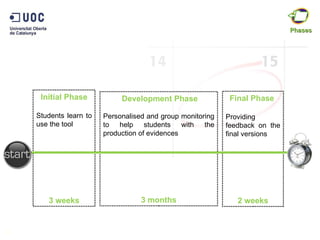
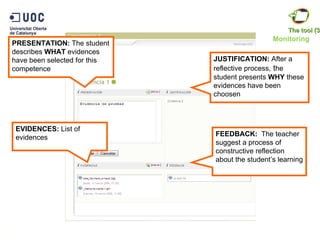
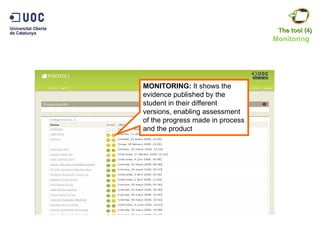
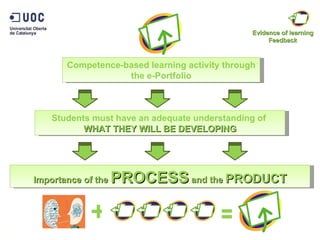
The document discusses the practical application of e-portfolios at the Open University of Catalonia, focusing on competence-based learning and assessment through a pilot program. It outlines the phases of e-portfolio implementation, the roles of students and teachers, and the importance of providing evidence for learning progress. The findings highlight the benefits of e-portfolios in facilitating peer feedback, self-reflection, and improving learning outcomes.