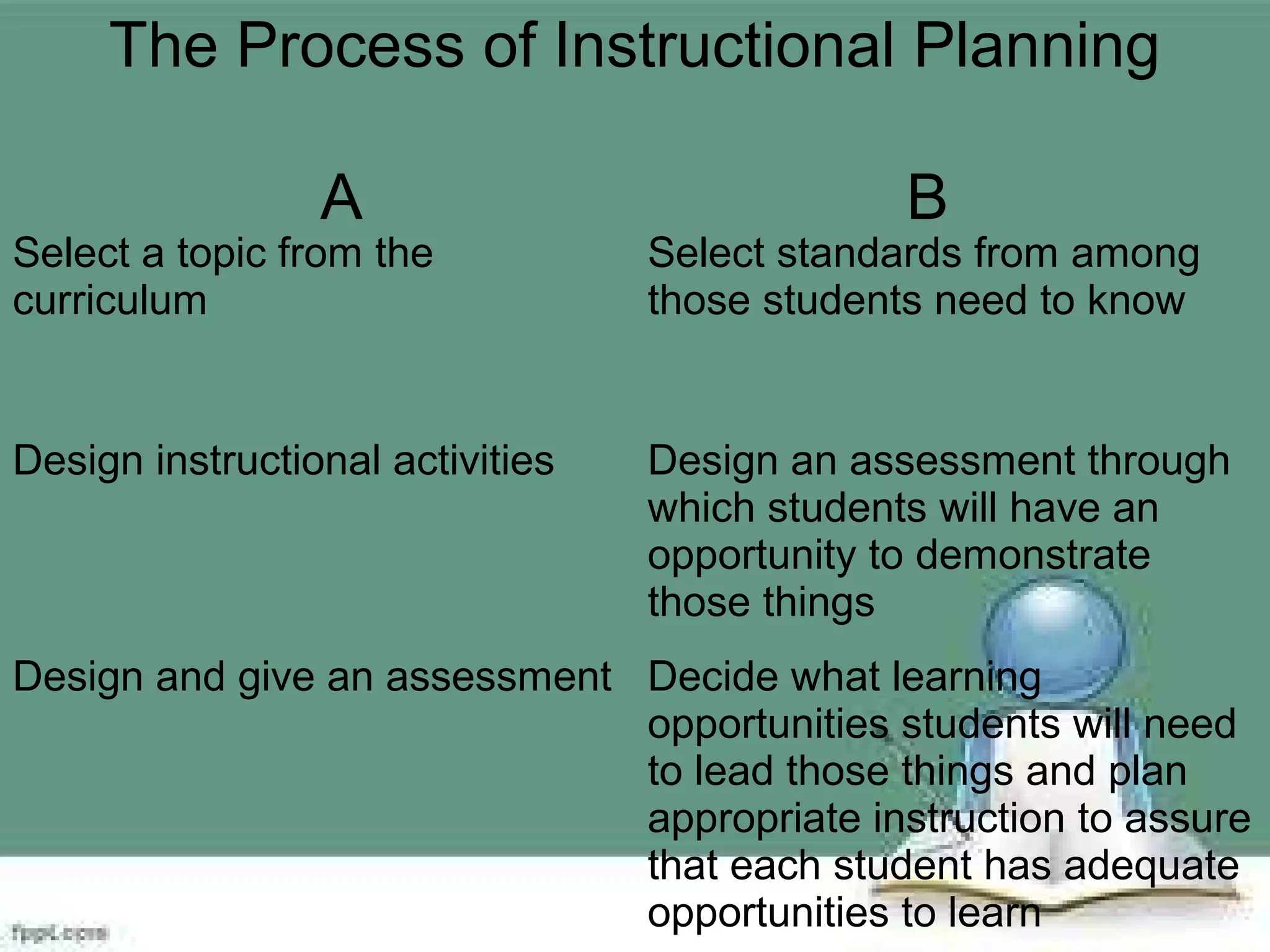
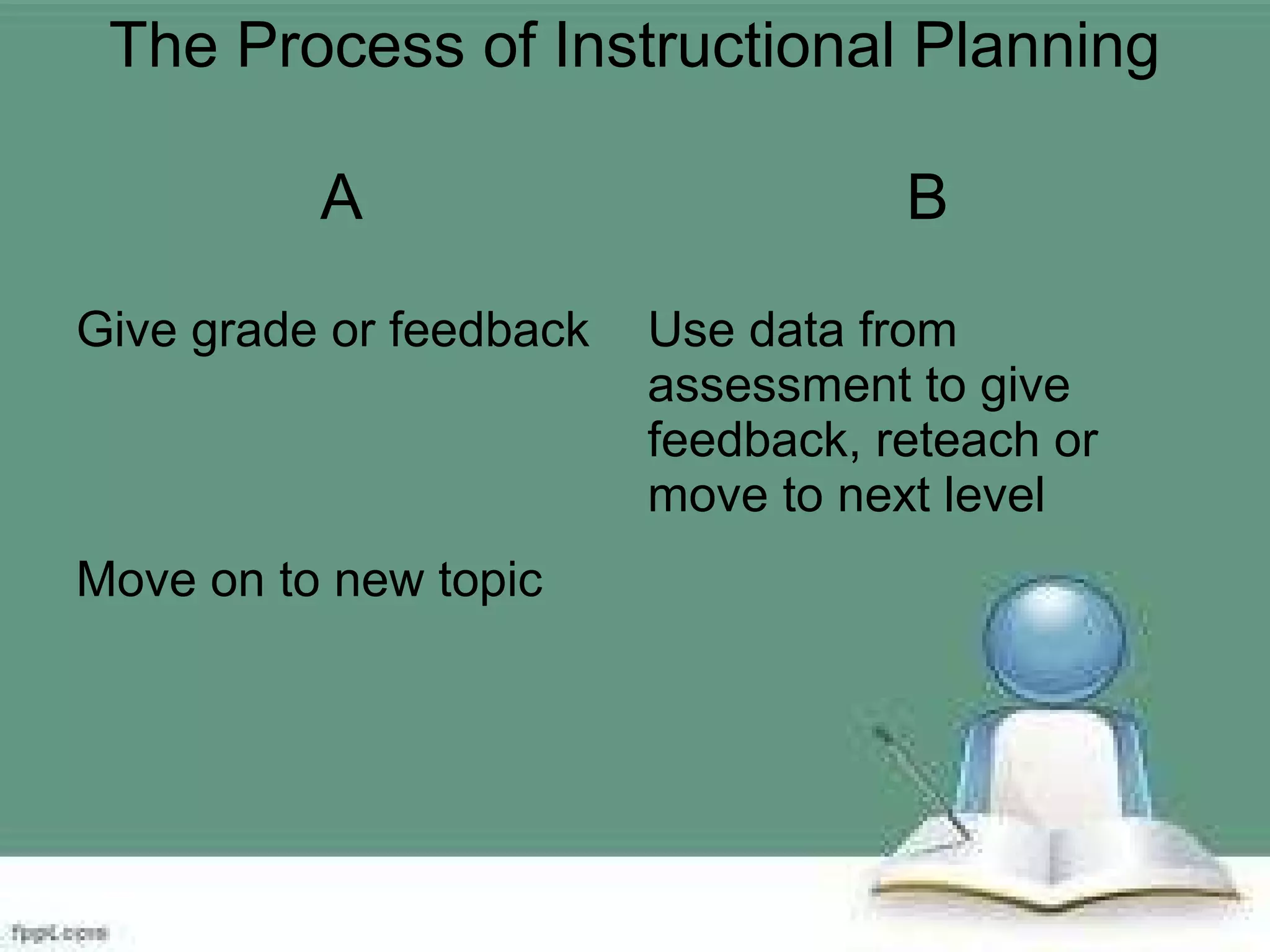
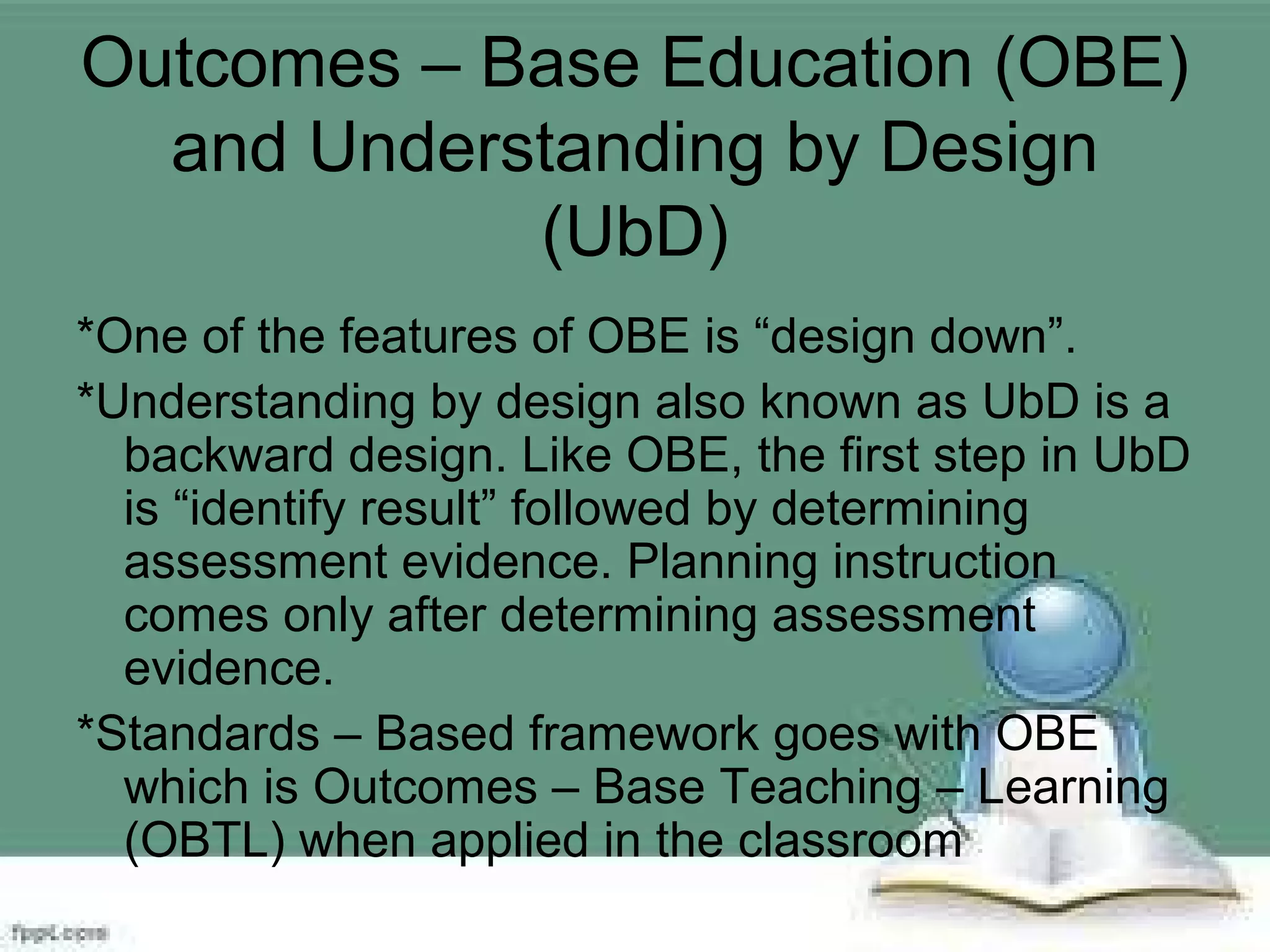
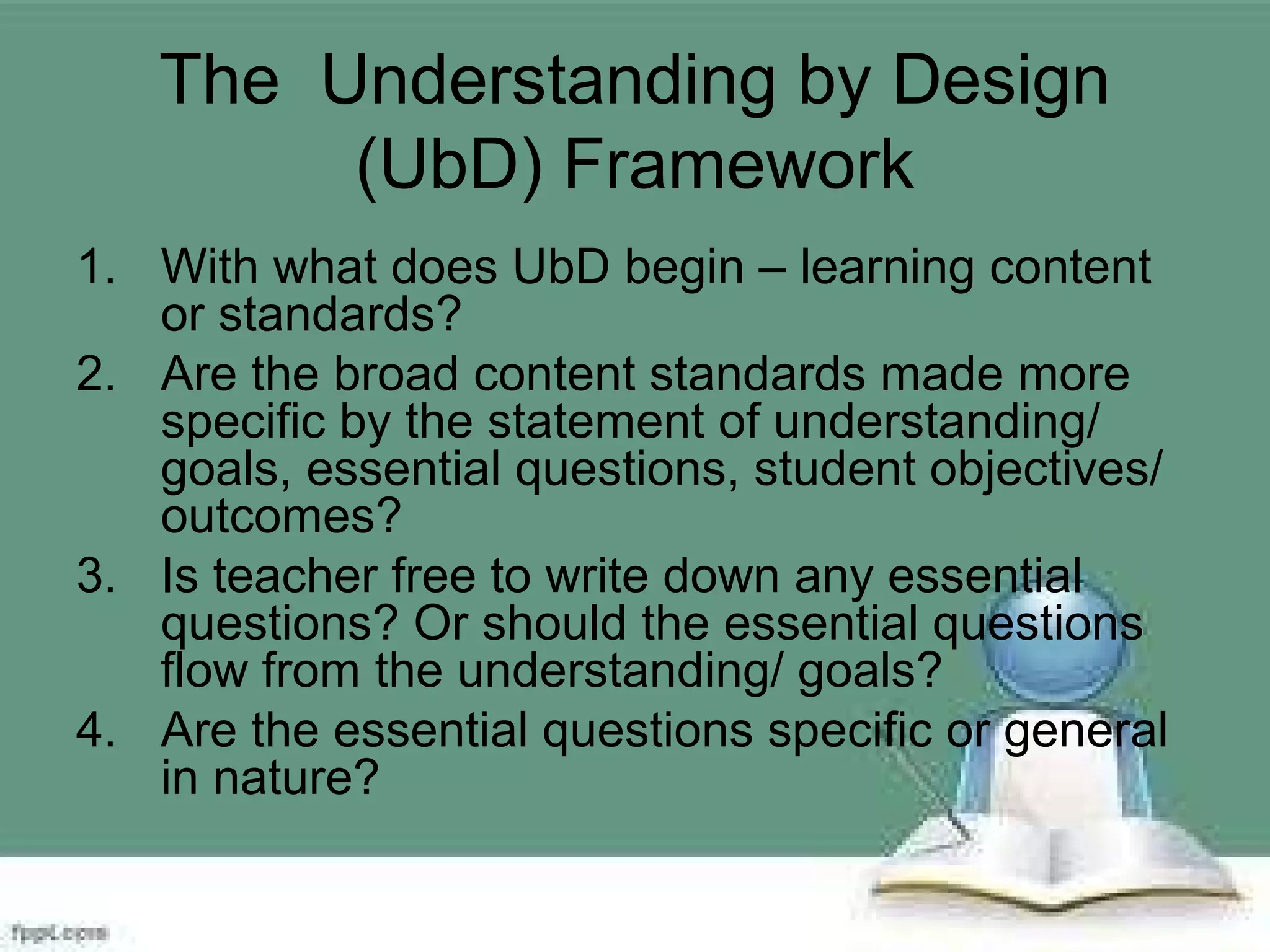
The document discusses instructional planning and development. It outlines the process of instructional planning which includes selecting standards and topics, designing instructional activities and assessments, giving assessments and using data to provide feedback and reteach. It also discusses outcomes-based education and understanding by design, which uses backward design starting with desired results and assessments. The three stages of understanding by design - stage 1 is desired results, stage 2 is assessment evidence, and stage 3 is the learning plan. Important elements of instructional planning include standards, curriculum goals, assessment, and utilizing assessment results. Several examples of lesson plan elements and formats are also provided.