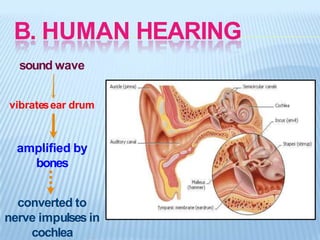
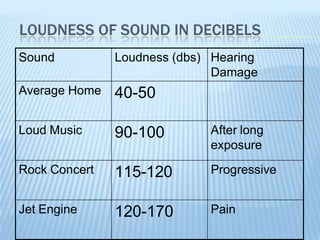
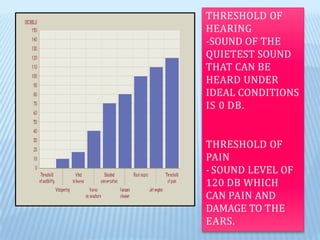
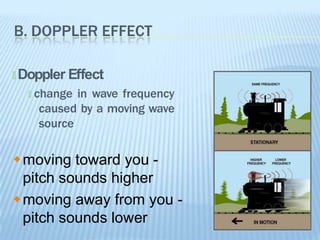
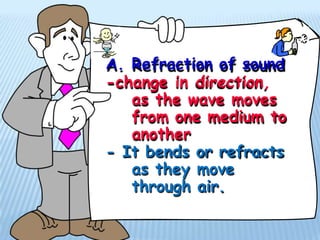
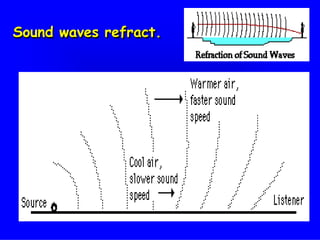
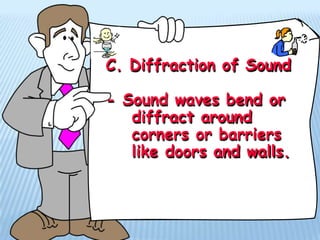
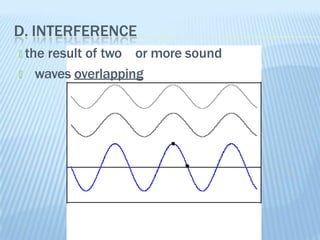
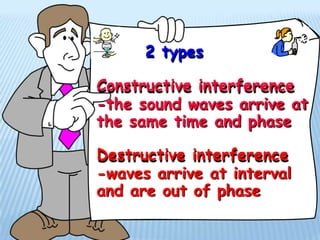
Sound is produced by vibrations that create variations in air pressure. It travels as longitudinal waves and can be characterized by properties like pitch, loudness, and timbre. The human ear detects sound waves, which vibrate the eardrum and cause nerve impulses that are interpreted by the brain. Sound waves can be reflected, refracted, diffracted, and undergo interference and resonance as they propagate through different media like solids, liquids, and gases. Musical instruments are classified as stringed, wind, or percussion based on how they produce sound vibrations.