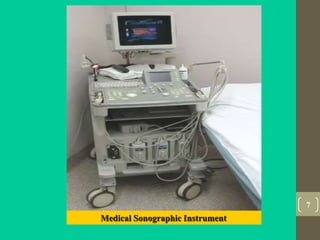
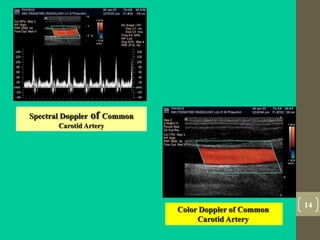
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to produce images of structures inside the body. It has several advantages over other imaging modalities like having no known long term side effects, being widely available, and being relatively inexpensive. Ultrasound works by using a transducer to send sound waves into the body which bounce off tissues and organs and are received by the transducer. The echoes are used to form images on screen in real time. While it is good for imaging soft tissues, ultrasound has limitations penetrating bone and imaging deep structures or when gas is present between the transducer and area of interest. It also requires an experienced operator to get high quality images.



![6
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity is the ability of some materials(notably crystals and
certain ceramics) to generate an electric potential[1] in response to applied
mechanical stress.
This may take the form of a separation of electric charge across the crystal
lattice.
The piezoelectric effect is reversible in that materials exhibiting the direct
piezoelectric effect
The effect finds useful applications such as the production and detection of
sound, generation of high voltages, and electronic frequency generation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sonopr-200316120846/85/Sonography-6-320.jpg)