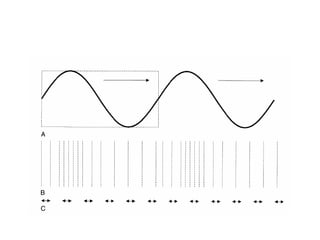
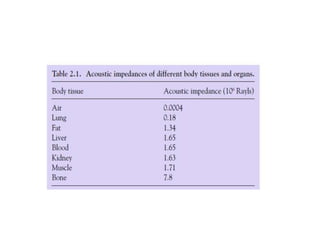
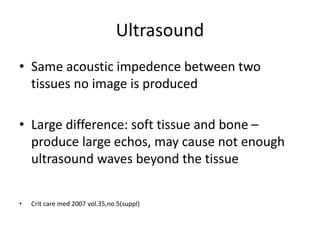
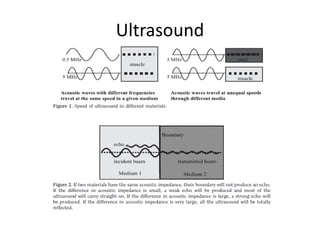
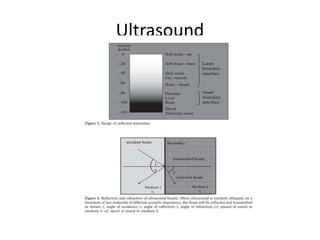
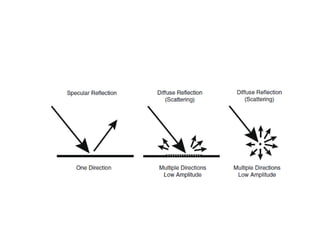
Ultrasound imaging is a cost-effective, portable, and radiation-free technique that provides real-time cross-sectional views for medical interventions. The document discusses the basic physics of ultrasound, emphasizing its properties such as frequency, acoustic impedance, and the behavior of ultrasound waves as they interact with different tissues. Key points include the attenuation of waves, piezoelectric crystals' role in generating ultrasound, and the importance of frequency for imaging resolution.