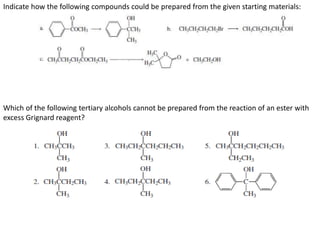
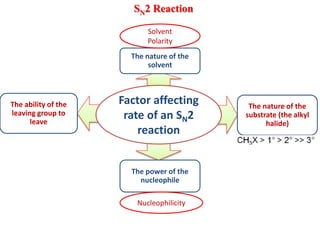
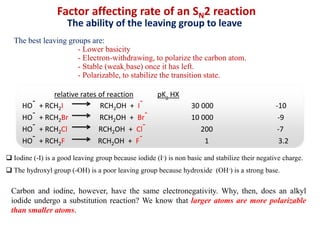
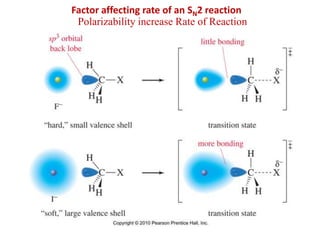
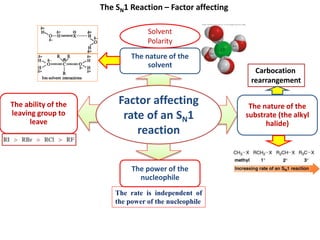
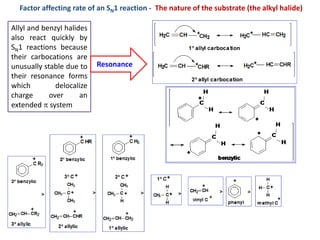
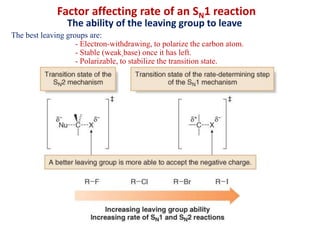
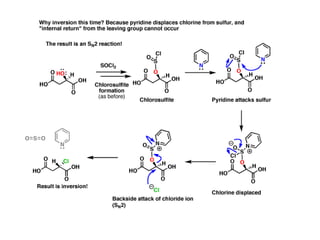
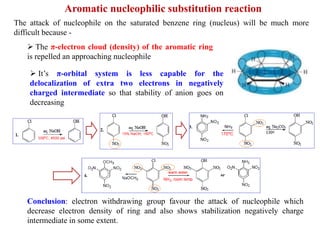
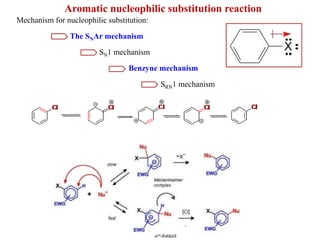
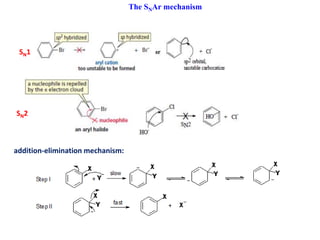
1. The document discusses alkyl halide reactions including SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. It describes factors that affect the rates of these reactions such as the substrate, leaving group, nucleophile, and solvent.
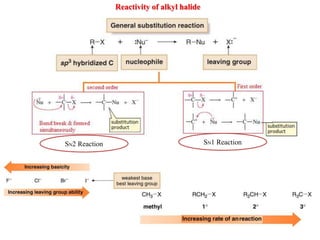
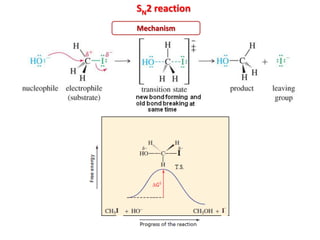
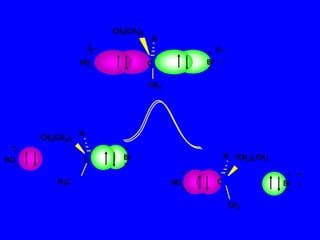
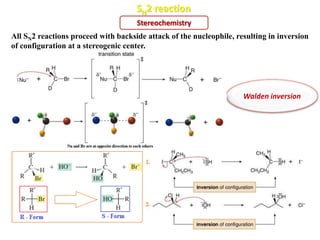
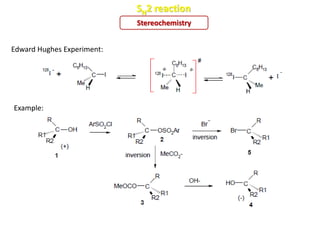
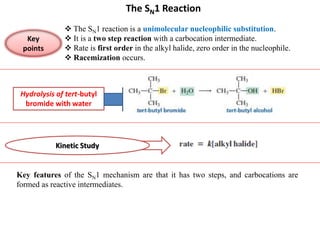
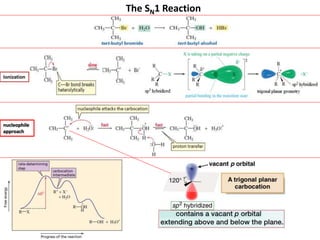
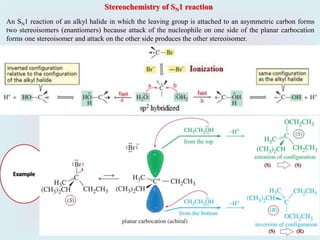
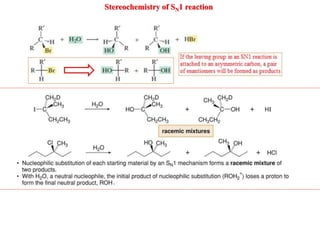
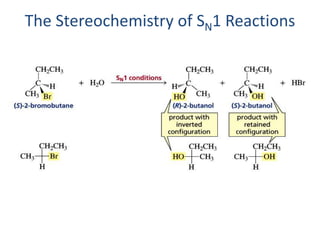
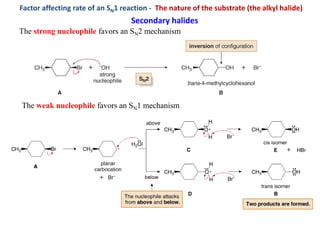
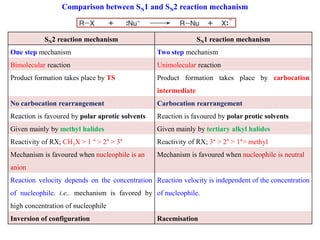
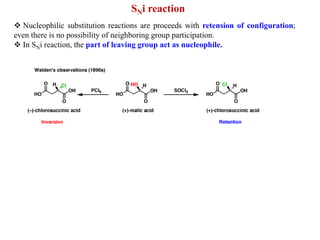
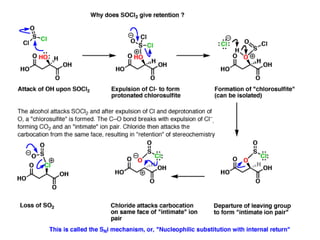
2. SN1 is a two-step reaction involving a carbocation intermediate. SN2 is a single-step reaction without an intermediate. SN1 reactions result in racemization while SN2 reactions cause inversion of configuration.
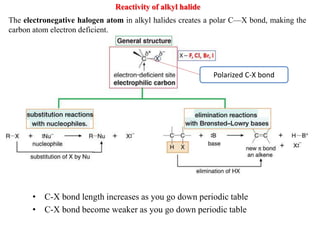
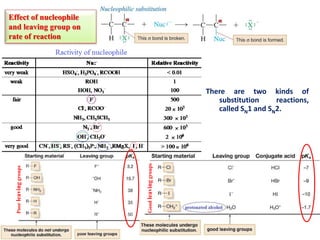
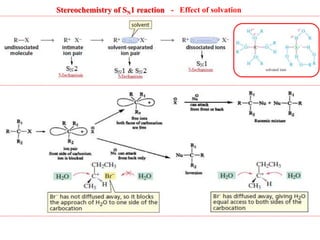
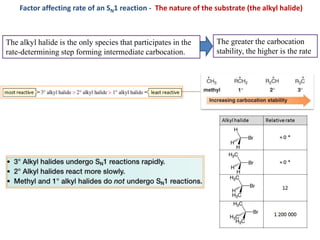
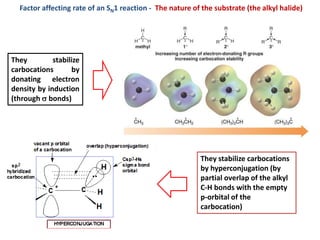
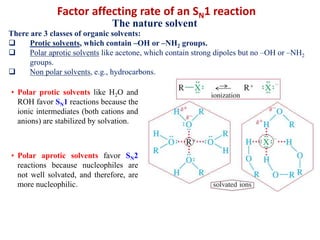
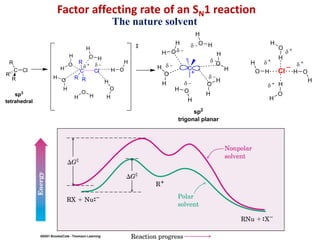
3. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo SN1 reactions most readily due to stable carbocation intermediates. Polar protic solvents favor SN1 while polar aprotic solvents favor SN2.


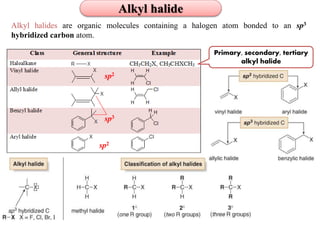

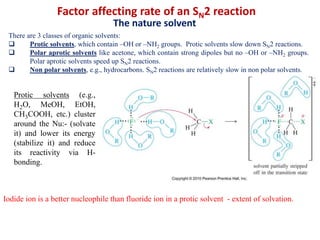
![ Polar Aprotic Solvents solvate the cation counterion of the nucleophile but not the nucleophile.
Examples include acetonitrile (CH3CN), acetone (CH3COCH3), dimethylformamide (DMF) [(CH3)2NC=OH],
dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO [(CH3)2SO], hexamethylphosphoramide, HMPA {[(CH3)2N]3PO} and
dimethylacetamide (DMA).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkylhalidereactions-180804134955/85/Alkyl-halide-reactions-22-320.jpg)

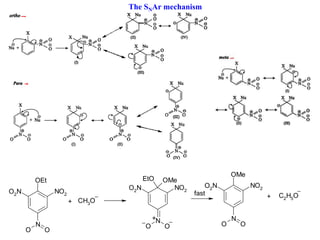
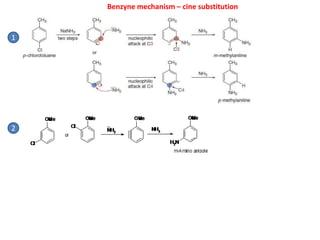
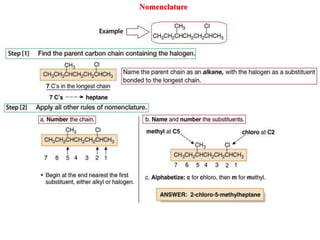
![Benzyne mechanism – cine substitution
Cl
H
NaNH2 NH3
NH2
NH2
+ + +
[Chlorobenzene] [Benzyne]
Strong bases - sodamide NaNH2 or certain metal alcoxides RONa (e.g. Me3COK)
Structure of benzyne:
Mechanism
Order of halide reactivity is Br > I > Cl >> F, when the reaction is performed with NaNH2
in liquid ammonia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alkylhalidereactions-180804134955/85/Alkyl-halide-reactions-46-320.jpg)