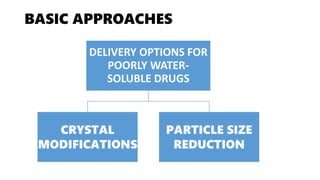
The document discusses formulation design approaches for poorly water-soluble drugs based on the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS). It describes the BCS, which categorizes drugs into four classes based on their solubility and permeability properties. Formulation strategies are then presented to improve the solubility and dissolution properties of BCS Class II and IV drugs, including crystal modifications like polymorphism and salt formation, particle size reduction through micronization and nanocrystallization, amorphization, cyclodextrin complexation, and self-emulsification systems. The selection of appropriate formulation approaches depends on understanding the drug's physicochemical properties and involves balancing efficacy, stability, and manufacturability.