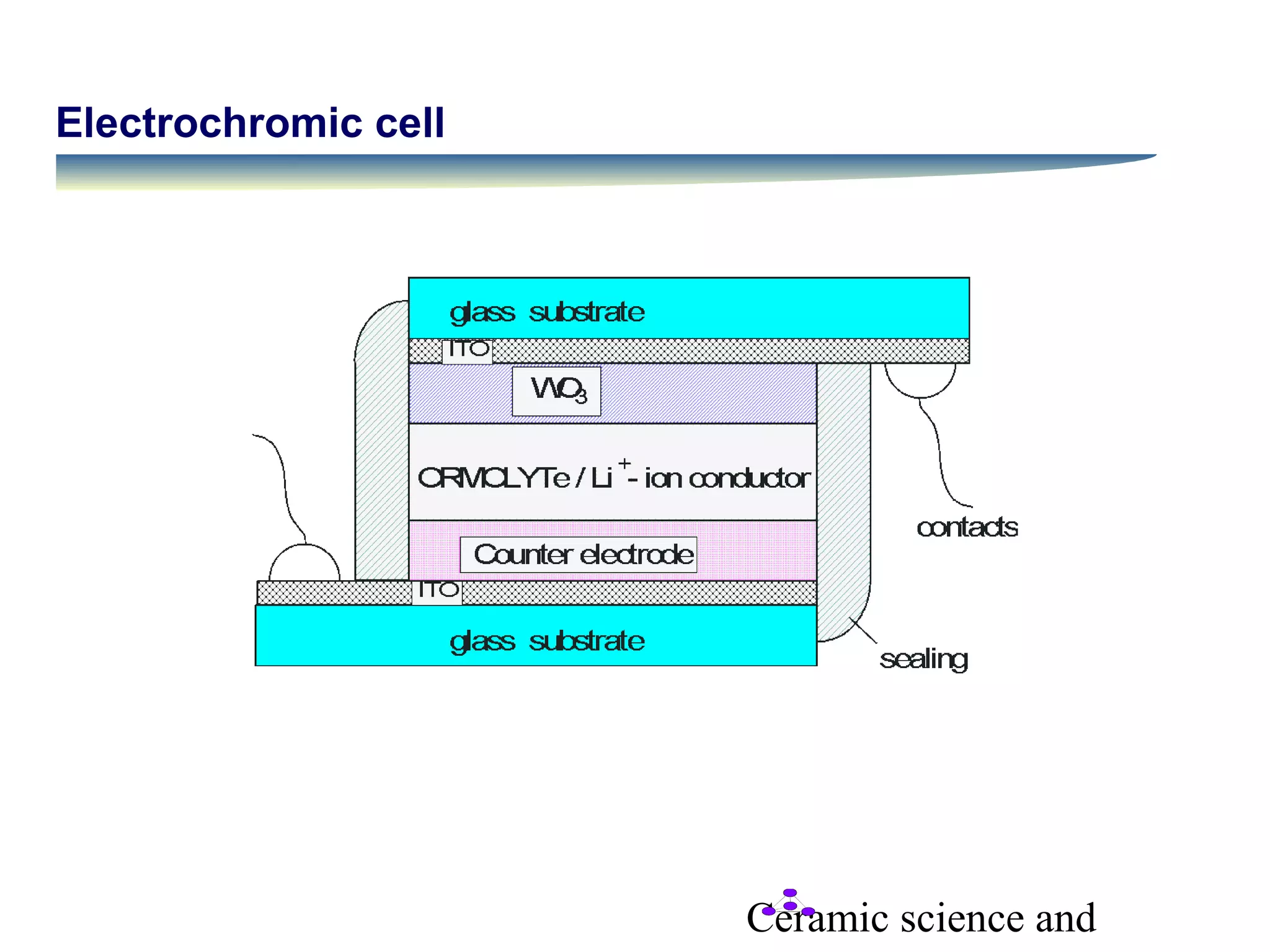
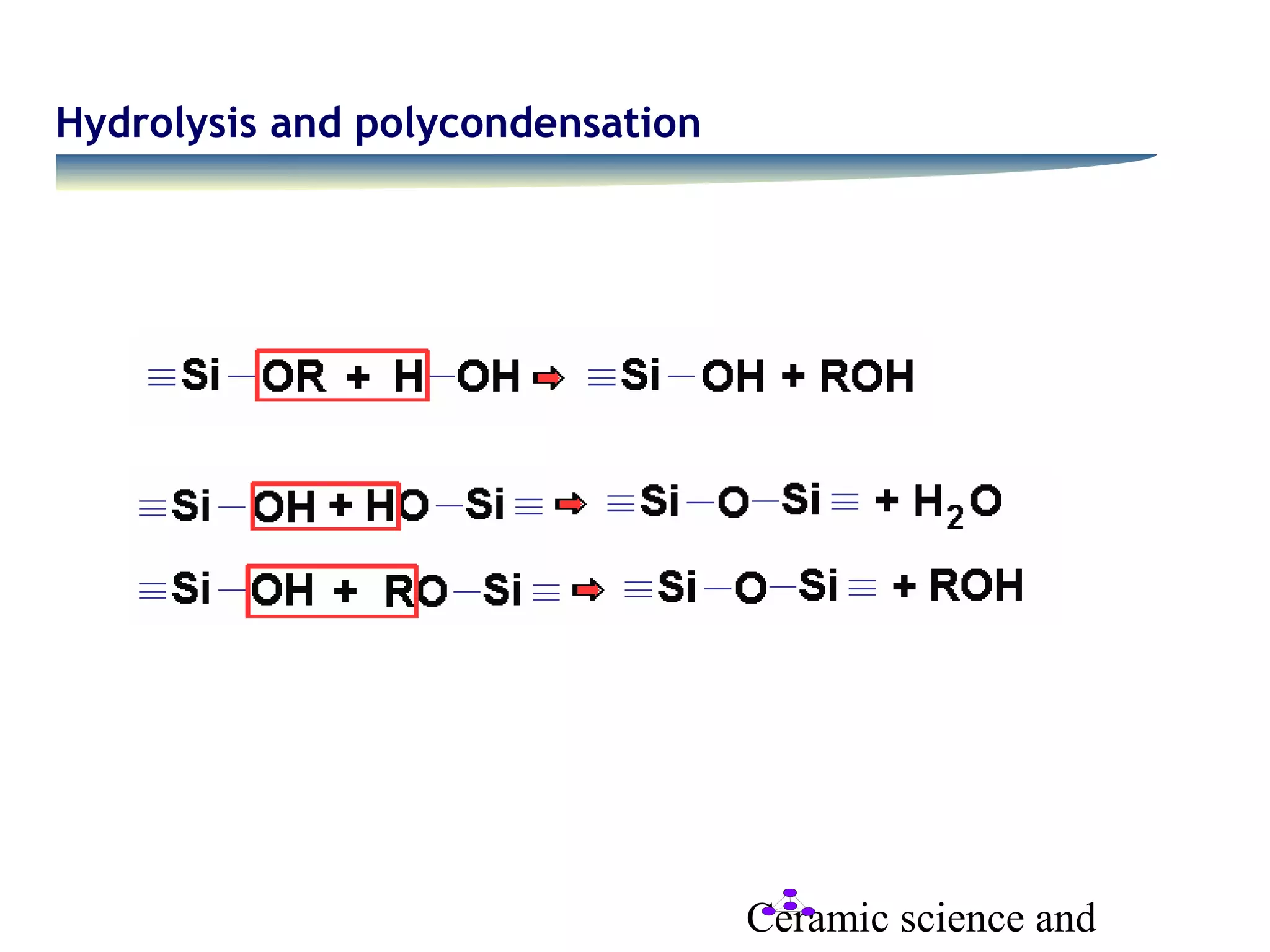
The document discusses several coating techniques used in ceramic science:
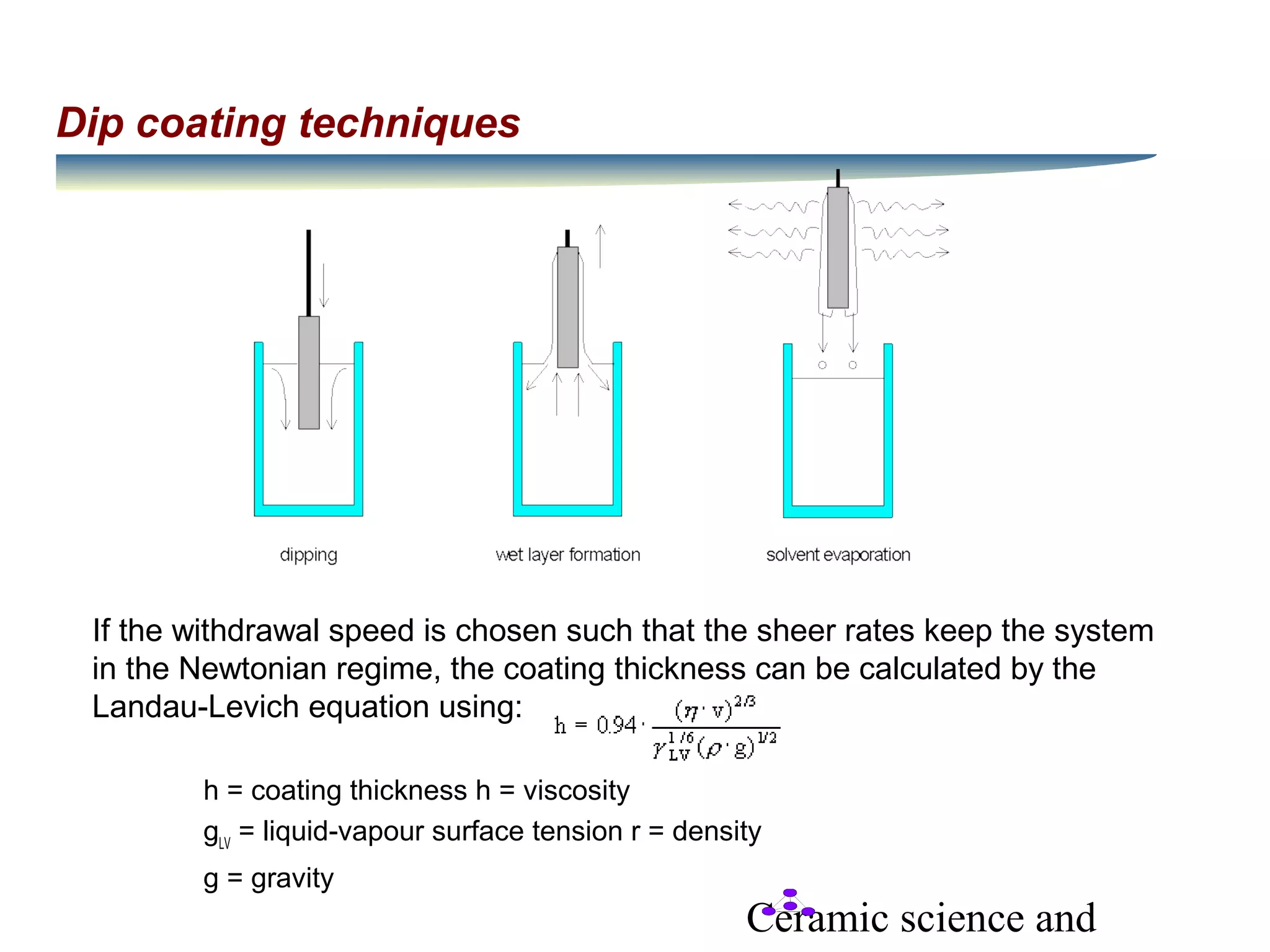
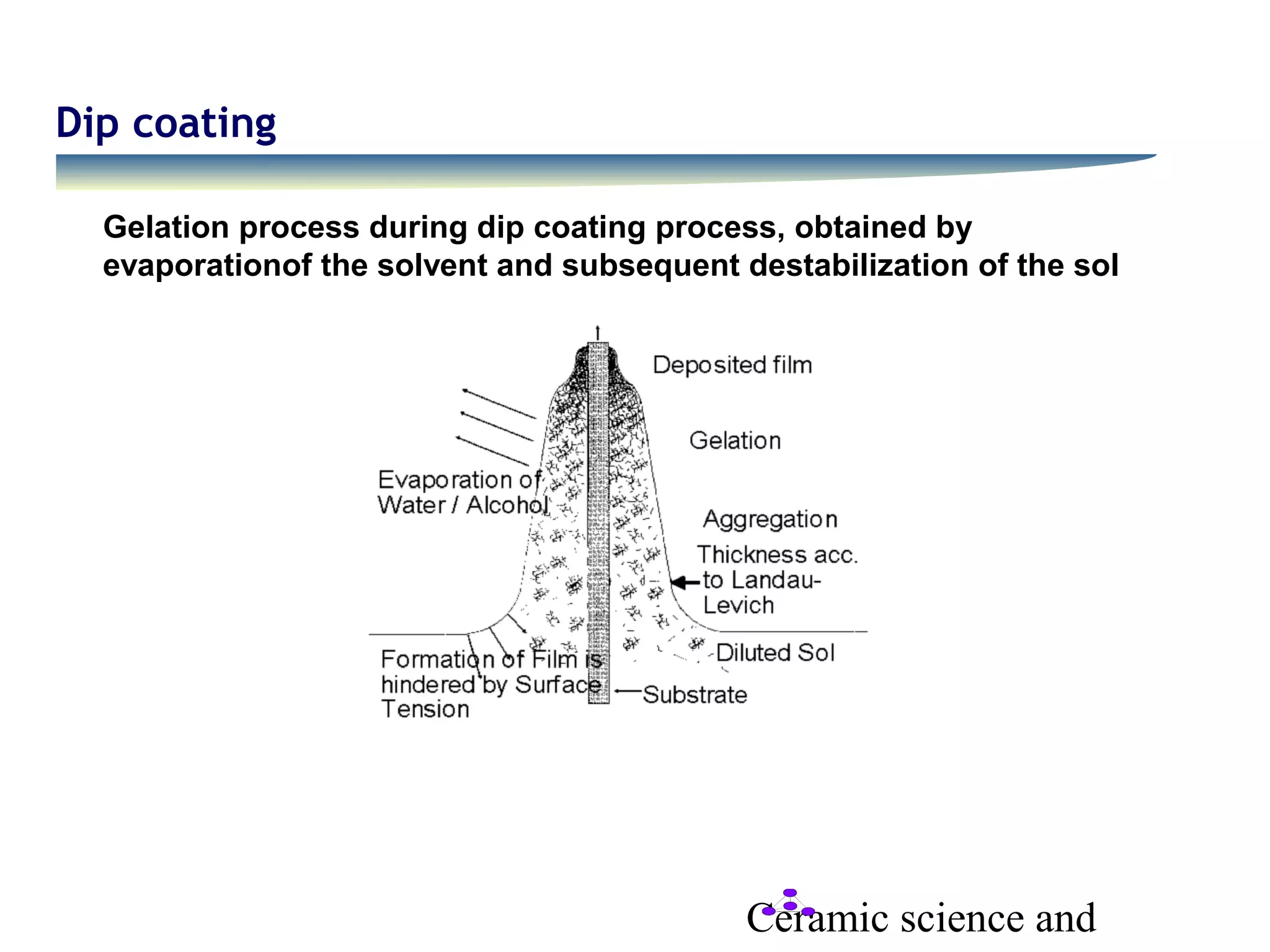
- Dip coating involves withdrawing an object from a liquid coating at a controlled speed, with coating thickness calculated by the Landau-Levich equation. Gelation then occurs through solvent evaporation and sol destabilization.
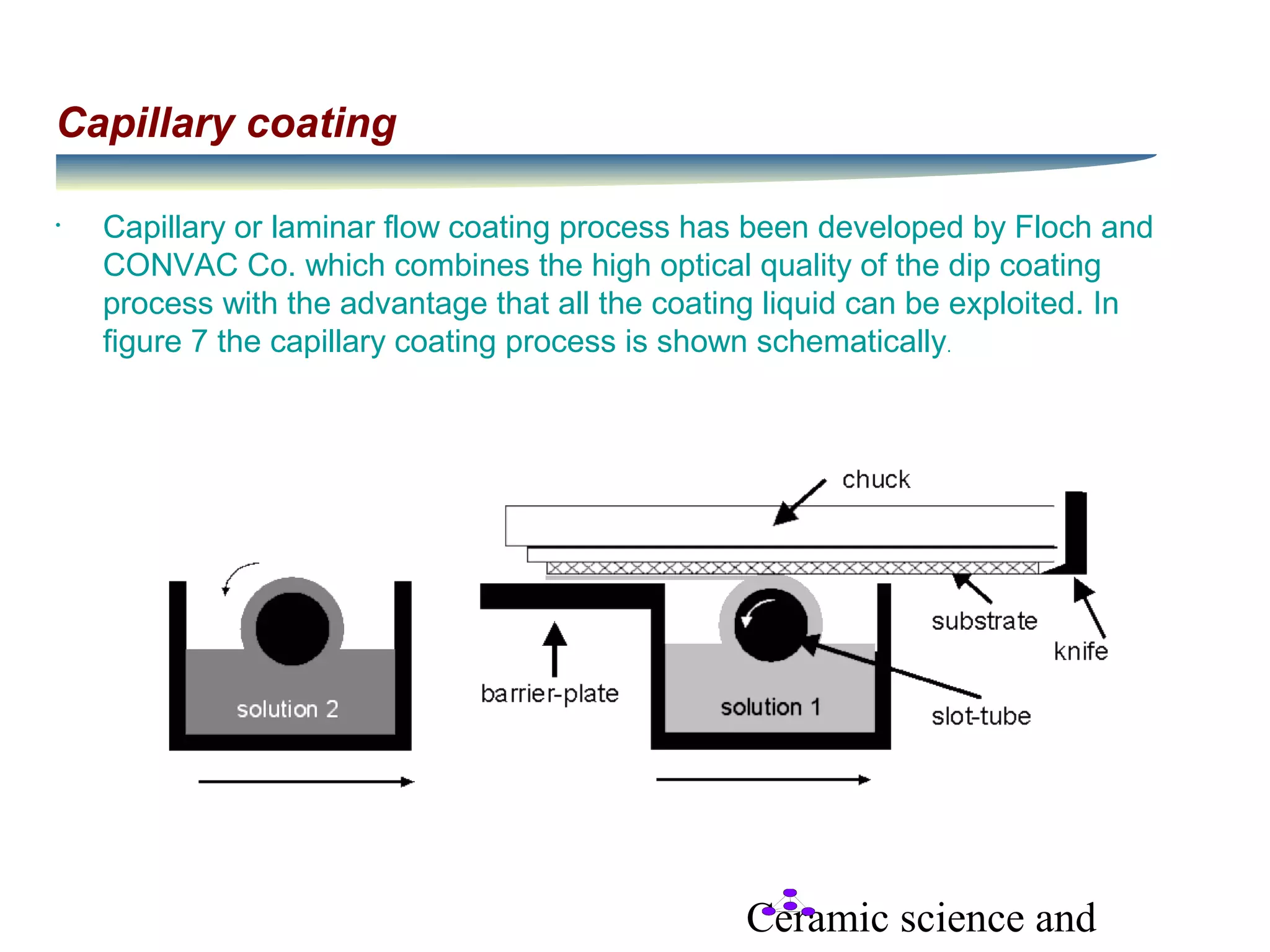
- Capillary coating combines the advantages of dip coating with utilizing all the coating liquid.
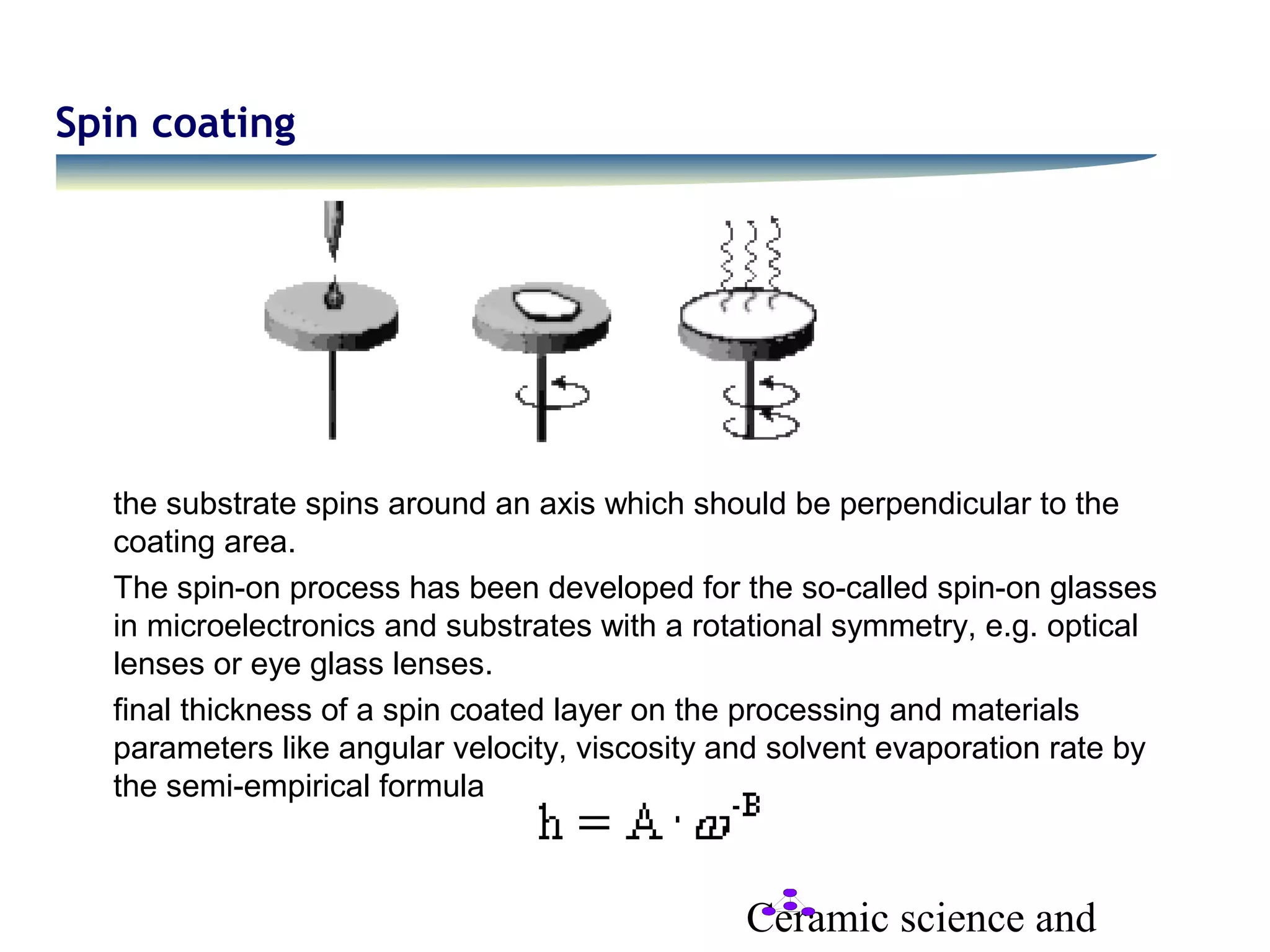
- Spin coating involves spinning a substrate to spread a liquid coating through centrifugal force, with final thickness determined by processing parameters in a semi-empirical formula.
- Compressive stress coatings through densified ceramic or glass coatings below the substrate glass transition temperature can improve glass strength by factors of 4.