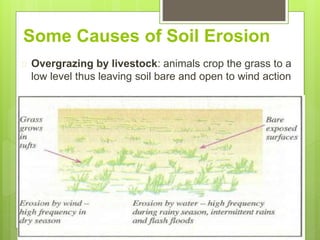
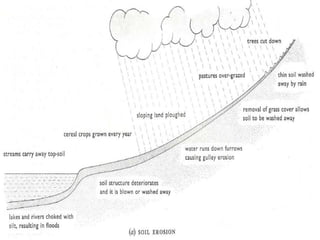
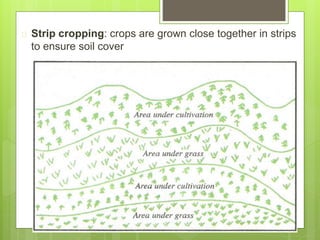
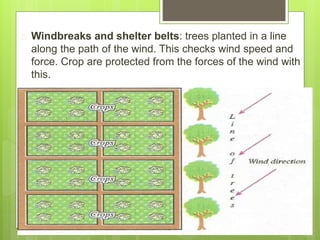
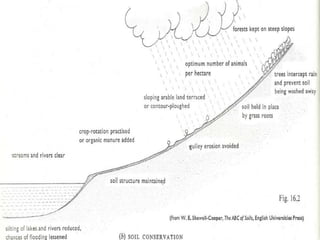
Soil erosion is the removal of topsoil from the land, primarily due to human mismanagement. There are three main types of erosion: sheet erosion caused by moving water, gully erosion from water in steep areas, and wind erosion in dry bare areas. Some key causes are overgrazing, cultivation on steep slopes, overcropping, and deforestation. To conserve soils, proper land management techniques can be used, including terracing, strip cropping, crop rotation, contour ploughing, reforestation, and windbreaks. These practices help reduce runoff and protect soil from heavy rainfall and winds.