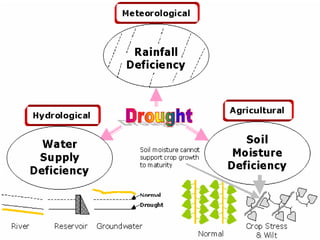
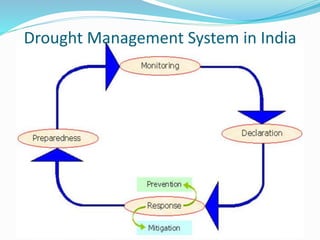
Drought is a period of below-average precipitation that results in prolonged water shortages. There are four main types of drought: meteorological, agricultural, hydrological, and socioeconomic. Causes of drought include low amounts of atmospheric water vapor, shifting air masses, human activities like deforestation and overfarming, and global warming. India has a drought management system that involves reporting from local gram panchayats up through state and national authorities. Over the past 200 years India has experienced many reported drought events.