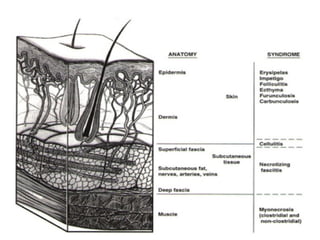
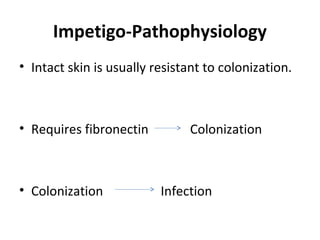
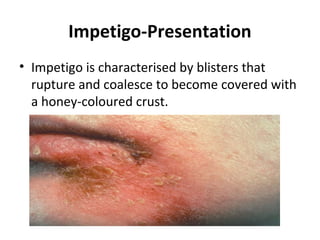
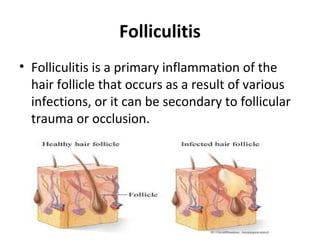
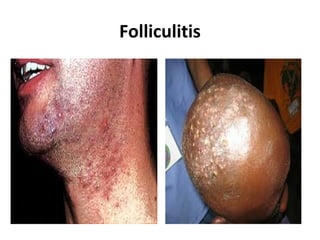
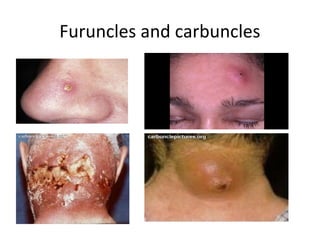
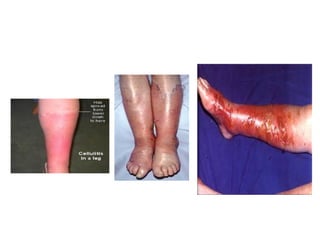
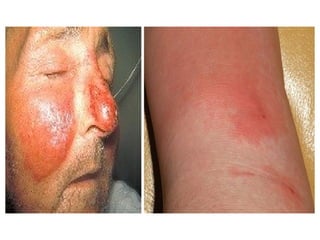
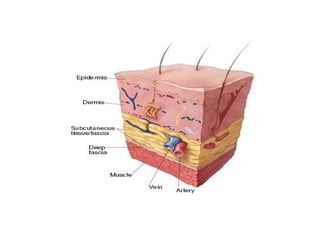
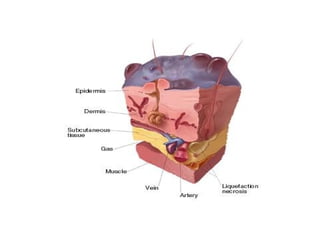
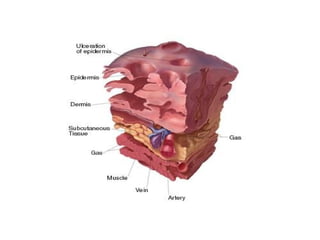
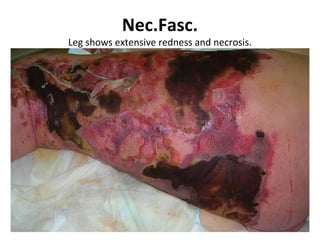
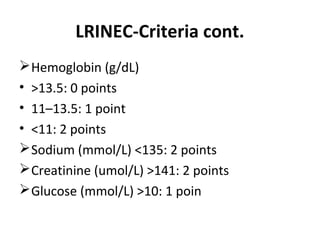
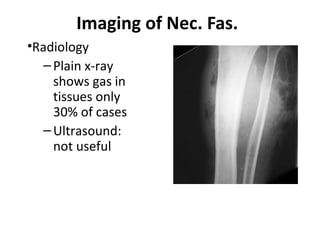
This document provides an overview of various soft tissue infections, including their presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. It discusses impetigo, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, erysipelas, necrotizing fasciitis, pyomyositis, and clostridial myonecrosis. The key points are: impetigo typically presents as blisters that rupture and form honey-colored crusts in children; cellulitis presents as warm, swollen, tender skin but lacks pus; necrotizing fasciitis is a severe infection requiring urgent debridement and antibiotics to treat widespread fascial necrosis; and clostridial myonecrosis following trauma can