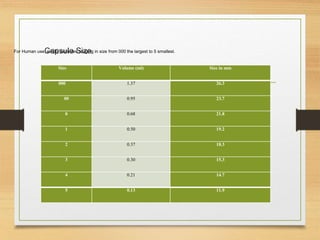
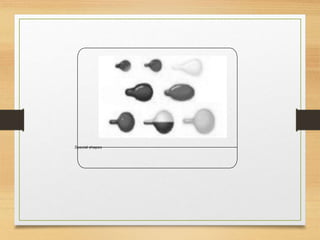
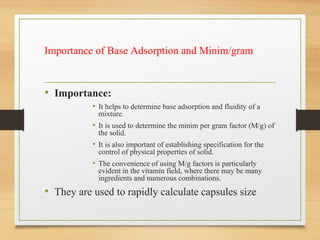
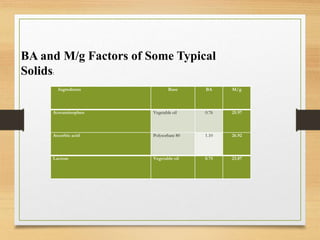
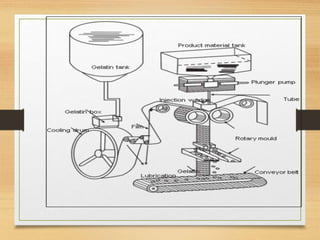
Soft gelatin capsules are solid dosage forms where liquid, paste or powder medications are enclosed in a soft gelatin shell. They are made from gelatin and a plasticizer like glycerin or sorbitol which gives them a higher moisture content than hard capsules. Common sizes range from size 000 to 5. Special shapes include tubes, ovals and oblong capsules. Soft gels are produced via plate, rotary die and reciprocating die processes which involve applying liquid mixtures to gelatin sheets to form continuous ribbons of half shells that are then filled and sealed. Quality is ensured through testing like dissolution, disintegration and content uniformity. Stability is monitored for moisture and physical changes over time. Soft gels