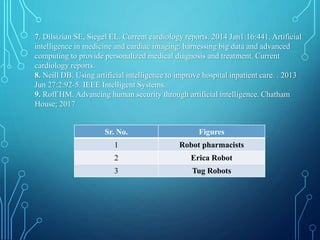
The document discusses the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in pharmacy, highlighting its applications in areas such as drug discovery, medication management, and patient care. It identifies both advantages, like improved efficiency and personalized medicine, and challenges, including data privacy and ethical issues regarding AI adoption in the pharmaceutical sector. The text also explores various tools and technologies used, such as robot pharmacists and predictive analytics, aimed at enhancing healthcare outcomes.