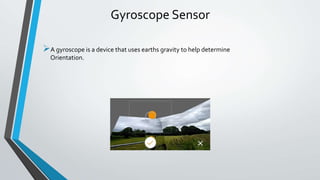
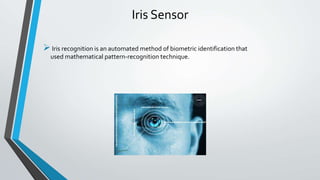
The document provides an overview of various smartphone sensors, including their functions and capabilities, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and fingerprint sensors. It highlights the role of these sensors in enhancing user interaction, security, and fitness tracking. Key sensors covered also include air gesture, humidity, ambient light, iris, magnetometer, motion, pedometer, proximity, heart rate, and IR blaster sensors.