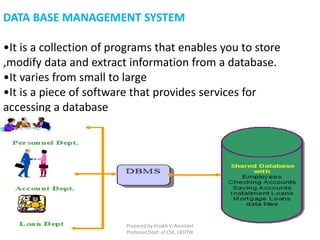
This document introduces databases and database management systems. It defines what a database is as interrelated data with controlled redundancy that can be used by different people independently. It lists advantages of databases over traditional file systems such as centralized control, reduced redundancy, avoiding inconsistency, enabling data sharing, enforcing standards, applying security restrictions, maintaining integrity, and balancing conflicting requirements. It also describes characteristics of data in databases, types of databases, components of a database management system, and the functions of those components.