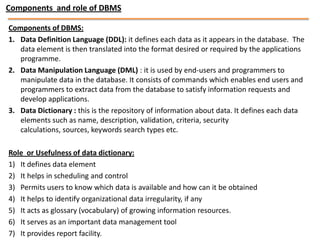
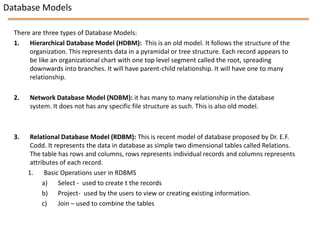
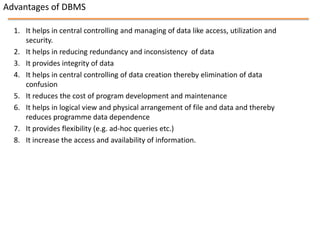
This document discusses database management systems and contains sections on databases, data warehousing, and data mining. It defines what a database and database management system are, and describes their components and advantages. It outlines three database models - hierarchical, network, and relational - and provides more details on the relational model. The document also defines data warehousing and lists its functions and benefits. Finally, it briefly introduces the topic of data mining.