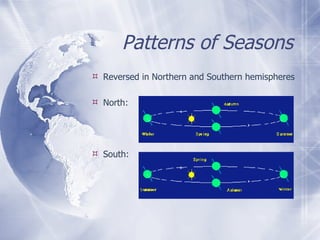
The document discusses weather, climate, seasons and temperature. It defines weather as the current atmospheric conditions including temperature, humidity and wind. Climate is the average weather conditions in a region over time. Seasons are the four natural divisions of the year - spring, summer, autumn and winter - which are caused by the Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun. Temperature is measured using a thermometer and determines how hot or cold substances are. Climate and seasons vary depending on a region's location.