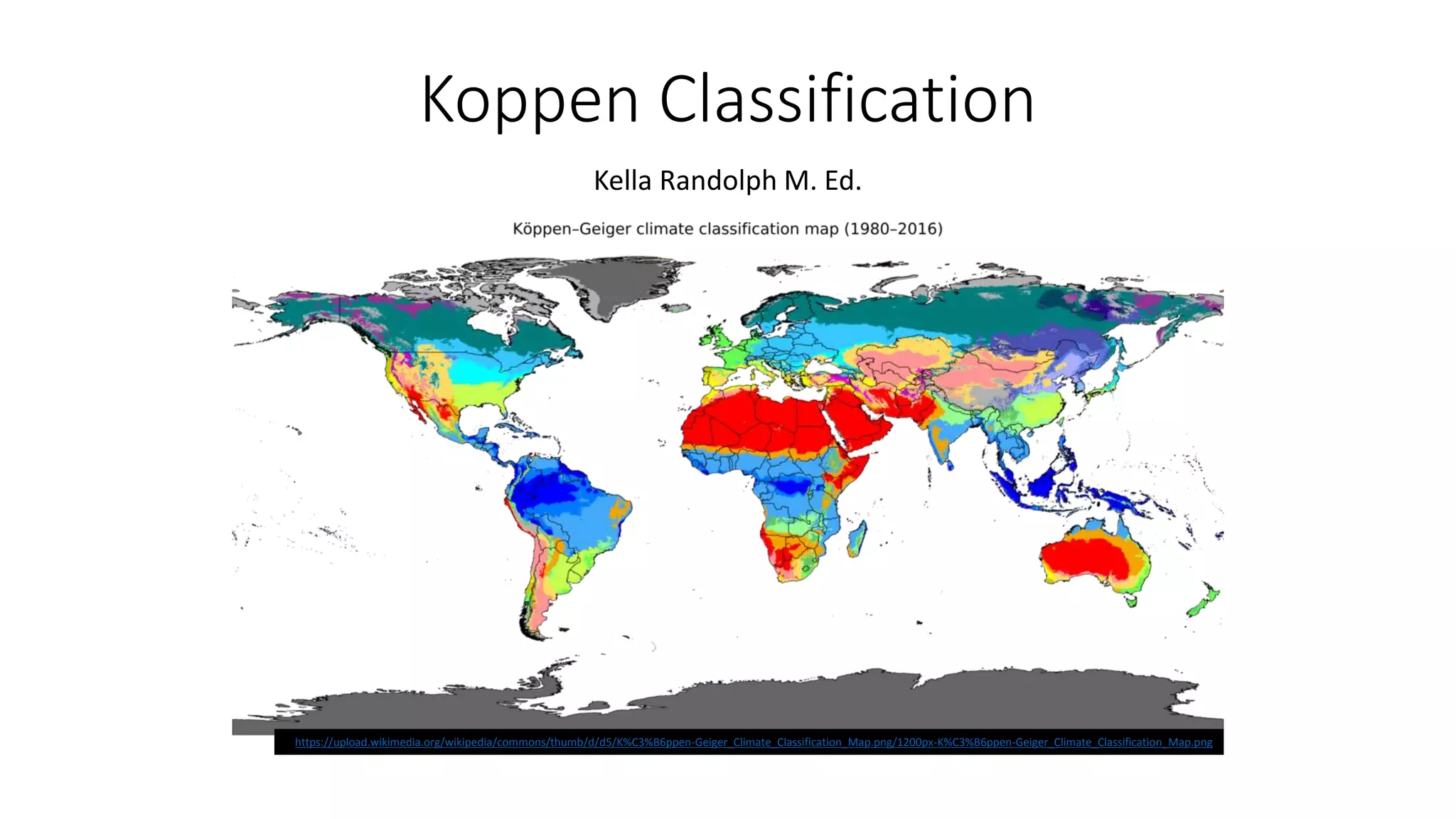
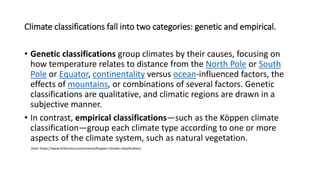
The document discusses the Köppen climate classification system, which was developed by German meteorologist Wladimir Köppen to categorize the world's climates based on temperature and rainfall. It outlines five major climate types (A, B, C, D, E) and their subcategories, as well as the genetic and empirical classifications of climates. Additionally, it describes various climatic characteristics and examples of flora and fauna for specific climate regions such as polar, dry, temperate, tropical, and continental.