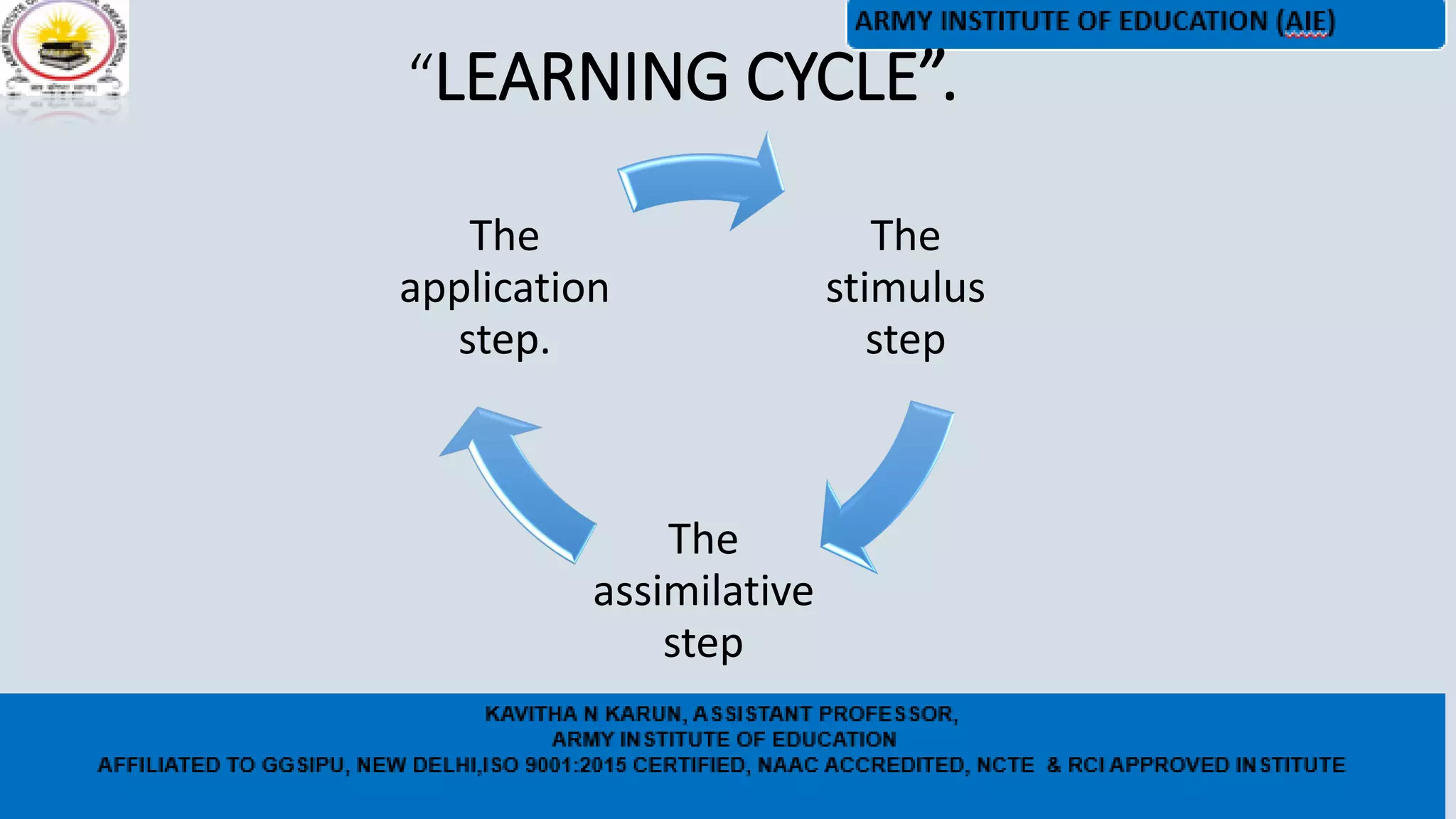
The document outlines the demonstration method of teaching, which involves exhibiting and demonstrating concepts through direct examples or instructional media. Key aspects of the demonstration method include careful planning, practicing the demonstration, developing an outline, ensuring student participation and visibility, following logical steps, and evaluating based on relevance, participation, handling of materials, and timing. Some disadvantages are that it is not hands-on, has limited viewing, and restricted pacing, but it can help connect theories to practice when done effectively.