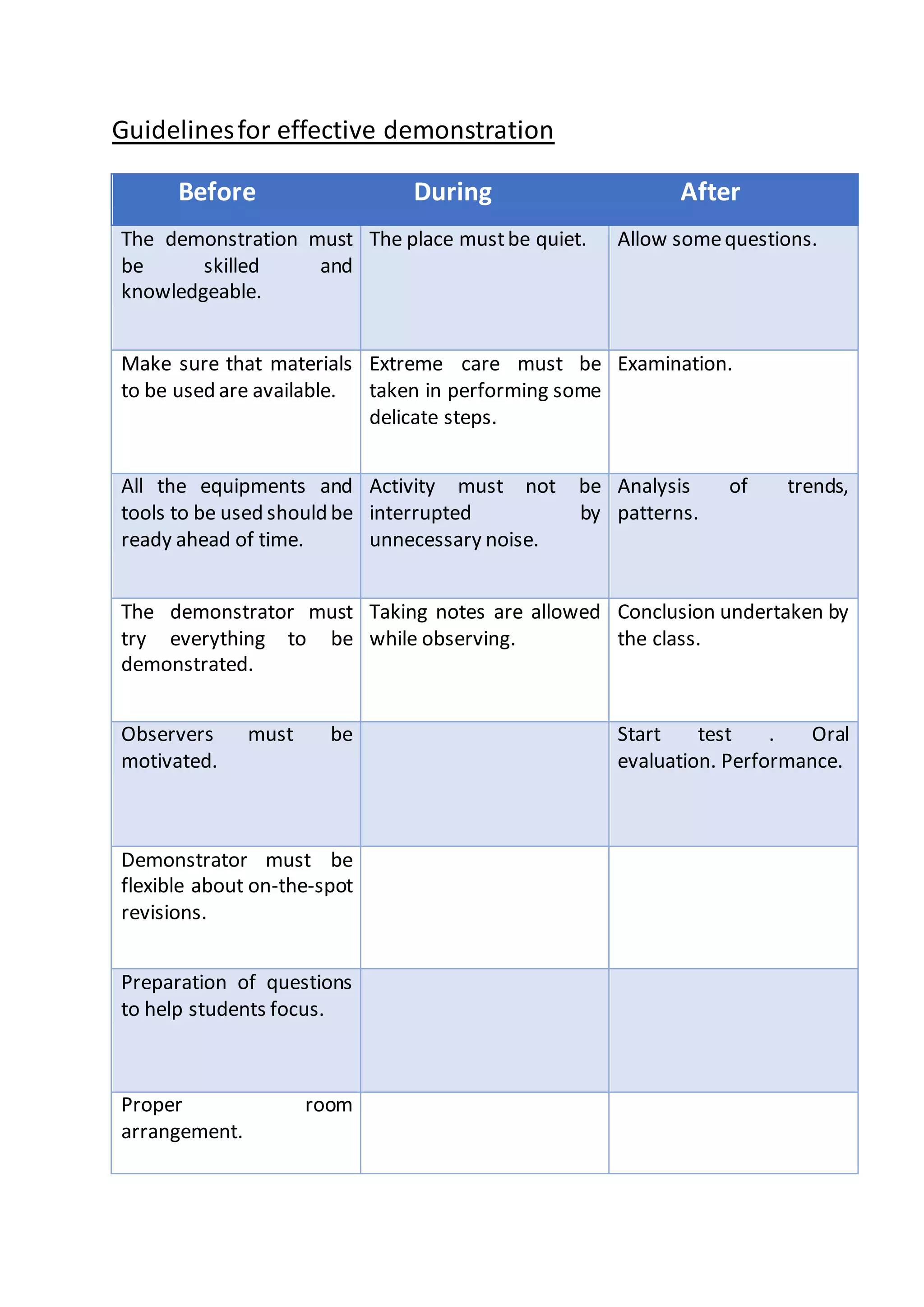
This document discusses the demonstration method of teaching. It defines demonstration as a planned manipulation of materials and equipment that allows learners to observe scientific principles and operations. The key aspects of demonstration are that it combines verbal explanation with a live display or use of apparatus. The demonstration method focuses on developing psychomotor and cognitive skills. It involves the teacher dominating the lesson by showing students how to operate equipment or demonstrate a process step-by-step. Guidelines for effective demonstration include planning thoroughly, using training aids, allowing hands-on practice, and providing examination and evaluation.