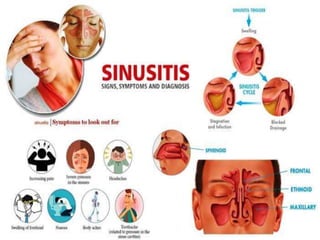
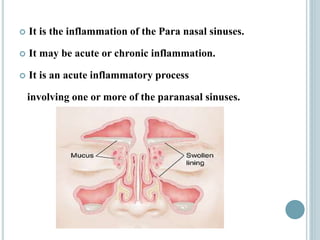
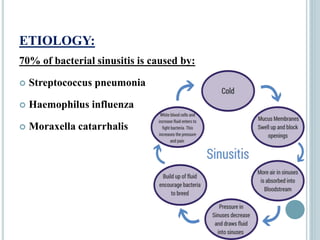
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergies or structural issues. It is classified as acute or chronic based on duration of symptoms. Acute sinusitis typically follows a viral upper respiratory infection and lasts less than 8 weeks. Chronic sinusitis causes long-term inflammation and symptoms lasting more than 8 weeks. Treatment involves antibiotics, nasal saline irrigation, decongestants and surgery in some chronic cases to improve drainage.