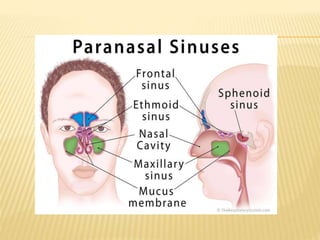
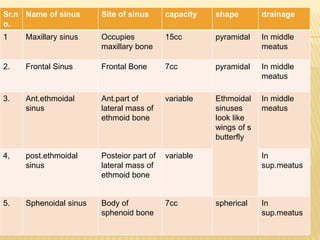
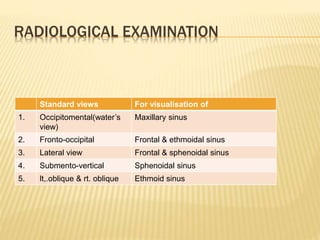
1) Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, the air-filled cavities around the nose. The four main sinus cavities are the maxillary, frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses.
2) Acute sinusitis is caused by viral or bacterial infection following a cold or allergy. Symptoms include facial pain, nasal congestion, and discolored nasal discharge. Maxillary sinusitis commonly involves pain in the cheek.
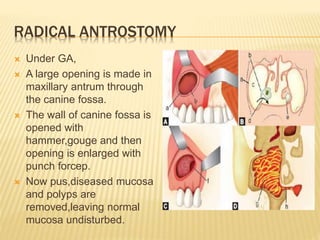
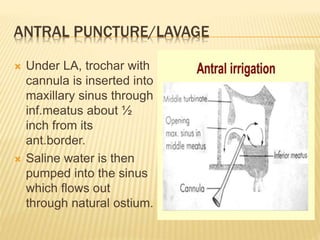
3) Treatment involves antibiotics, nasal decongestants, pain relievers, and surgery if symptoms persist. Surgical treatments include antral puncture to drain pus from the maxillary sinus or functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Comp