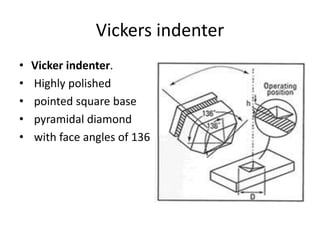
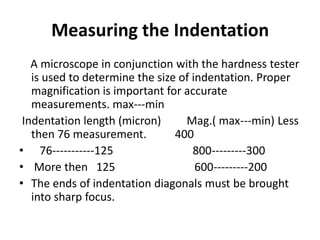
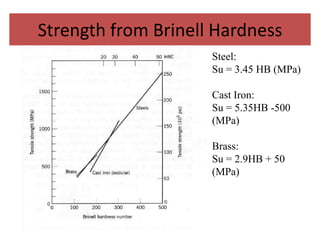
Micro hardness testing involves forcing a diamond indenter with a specific geometry into the surface of a test piece under a small load, then using a microscope to measure the resulting indentation to determine the hardness; there are three main types of tests that differ by the indenter shape and how indentation size is measured; micro hardness testing is useful for measuring small parts, surface layers, and the hardness of individual micro-constituents.