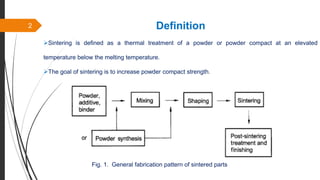
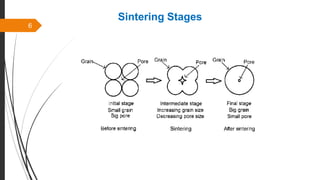
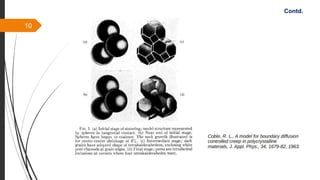
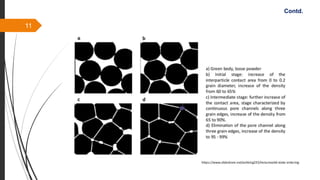
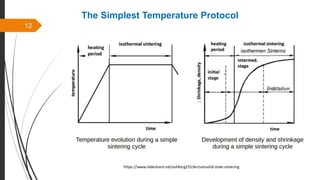
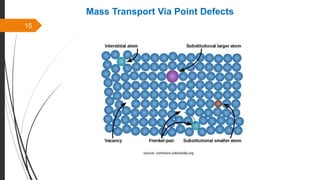
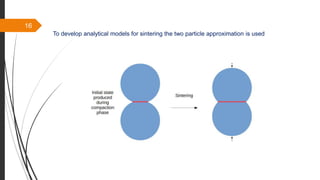
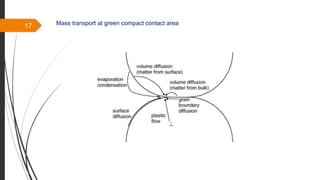
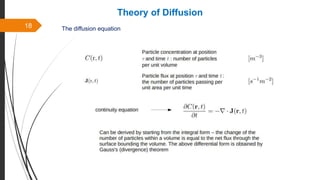
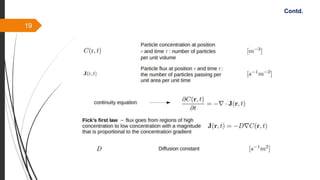
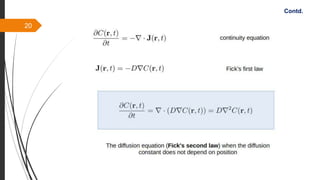
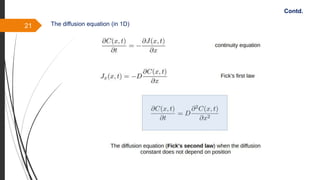
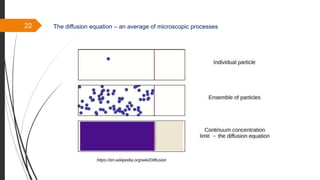
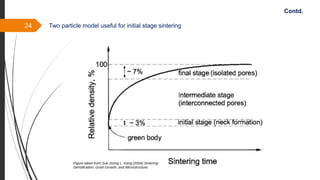
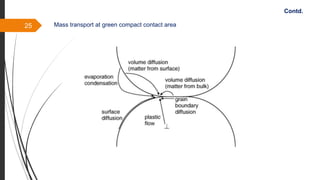
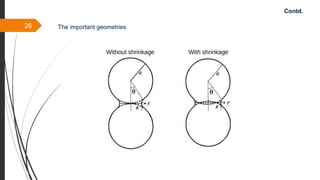
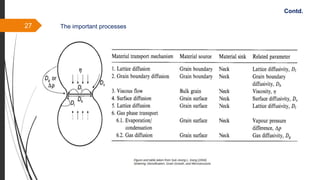
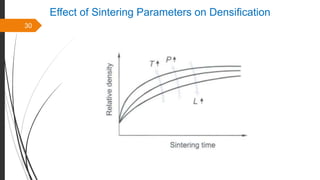
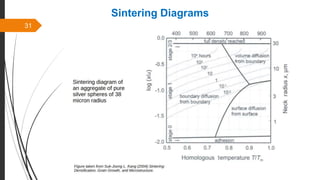
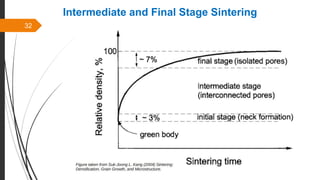
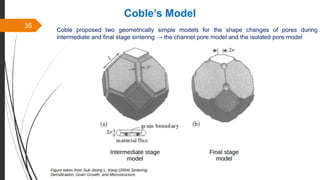
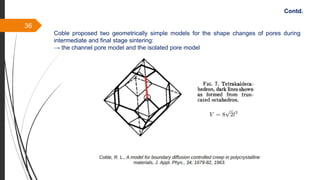
The document provides an overview of the sintering process in powder metallurgy, detailing its definition, types, parameters, and stages involved in sintering. It discusses the initial, intermediate, and final stages of sintering, along with factors affecting densification, such as particle size, pressure, and composition. Additionally, it references key models used to understand and analyze the sintering process.