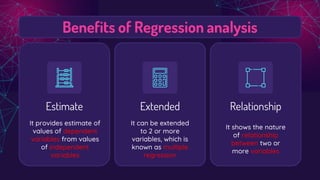
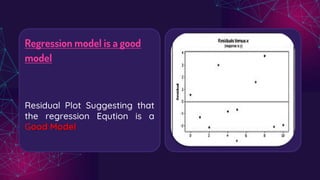
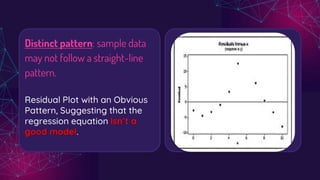
This document provides an overview of simple linear regression. It defines regression as measuring the average relationship between two variables. Regression allows estimation and prediction of a dependent variable from an independent variable. The key aspects covered include the linear regression equation Y = a + bX, where a is the Y-intercept and b is the slope. Residuals, which represent prediction errors, are also discussed. A residual plot is used to evaluate the appropriateness of the regression model by examining patterns in the residuals.