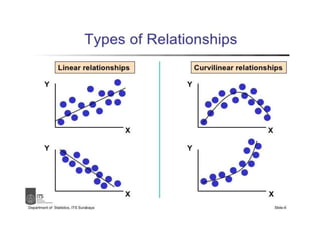
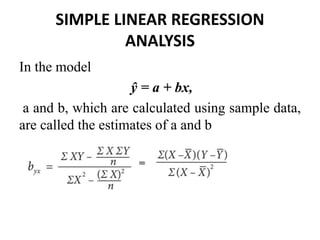
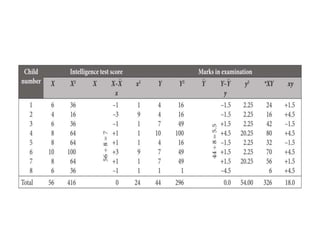
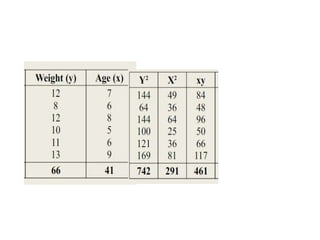
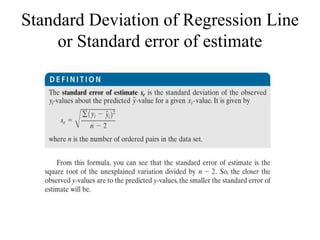
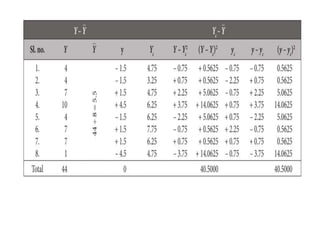
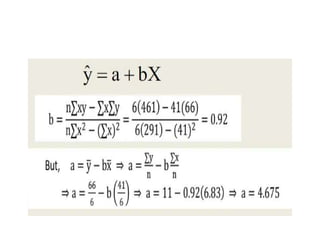The document provides an overview of simple and multiple regression models, highlighting their definitions and key components, including independent and dependent variables. It explains linear regression's straight-line relationship, the significance of the regression equation, and how to interpret the slope and intercept. Additionally, it discusses the error sum of squares and the coefficient of determination (r2) in the context of assessing the quality of a regression model.