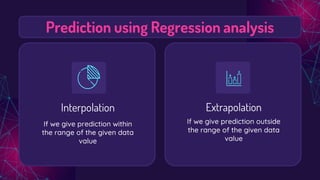
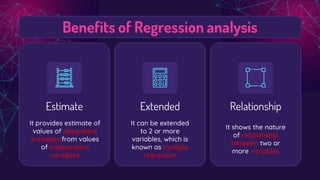
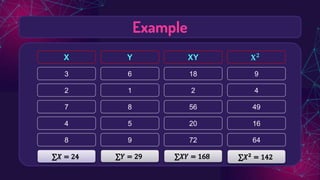
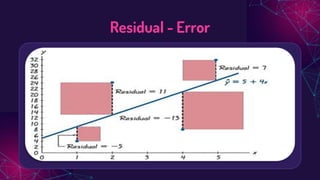
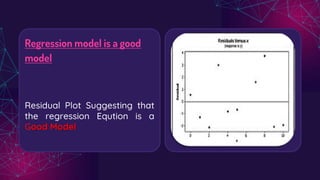
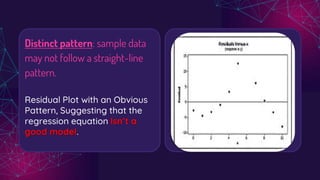
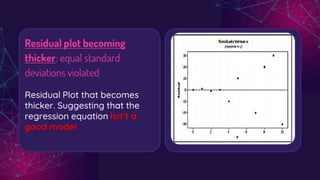
The document discusses regression analysis, highlighting the difference between interpolation and extrapolation when predicting values. It explains the linear regression equation, the least squares method to determine parameters, and the significance of residuals in assessing model accuracy. Additionally, it describes how to interpret residual plots to evaluate the suitability of a regression model.