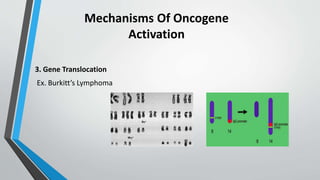
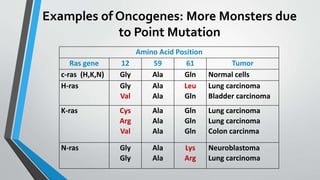
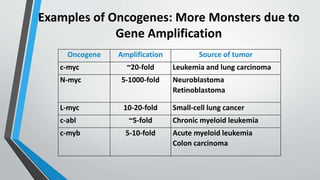
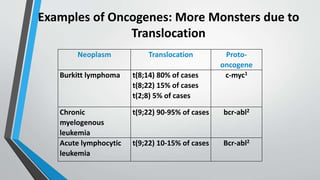
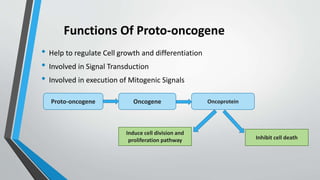
Oncogenes are genes that can transform normal cells into tumor cells, typically arising from mutations or increased expression of proto-oncogenes. Activation mechanisms include point mutations, gene amplification, and chromosomal translocations, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and various cancers. Examples of oncogenes include c-myc, h-ras, and bcr-abl, each associated with specific malignancies.




![Mechanisms Of Oncogene
Activation
1. Point Mutation
H-ras [codon 12]
Normal CGC Gly
Bladder cancer CTC Val
2. Gene Amplification
Double minutes
HSRs
Normal copy Multiple copies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbt-615pptoncogeneashfaq-191110122440/85/Oncogene-7-320.jpg)