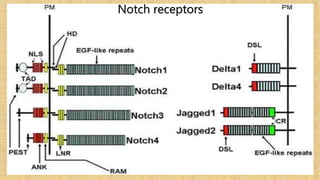
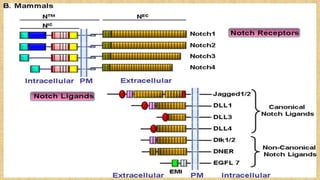
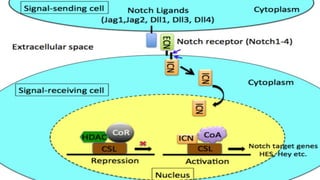
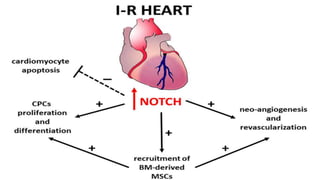
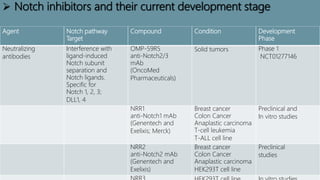
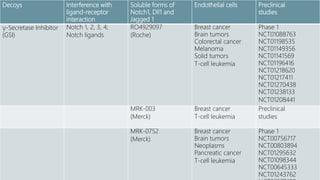
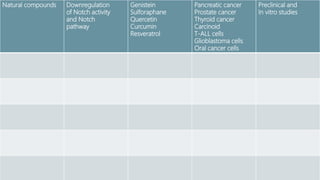
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling system that regulates cell differentiation, proliferation, and fate determination during embryonic and adult development. It involves transmembrane Notch receptors that are activated via cell-cell contact with Notch ligands, leading to proteolytic cleavage and release of the Notch intracellular domain which enters the nucleus to regulate gene expression. Notch signaling plays important roles in various processes including neurogenesis, cardiovascular development, and lymphocytic leukemia, where deregulation of Notch signaling can promote cancer. Inhibitors of Notch signaling such as gamma secretase inhibitors are being investigated as potential cancer therapies but have shown limited efficacy due to off-target effects.