Embed presentation
Downloaded 63 times

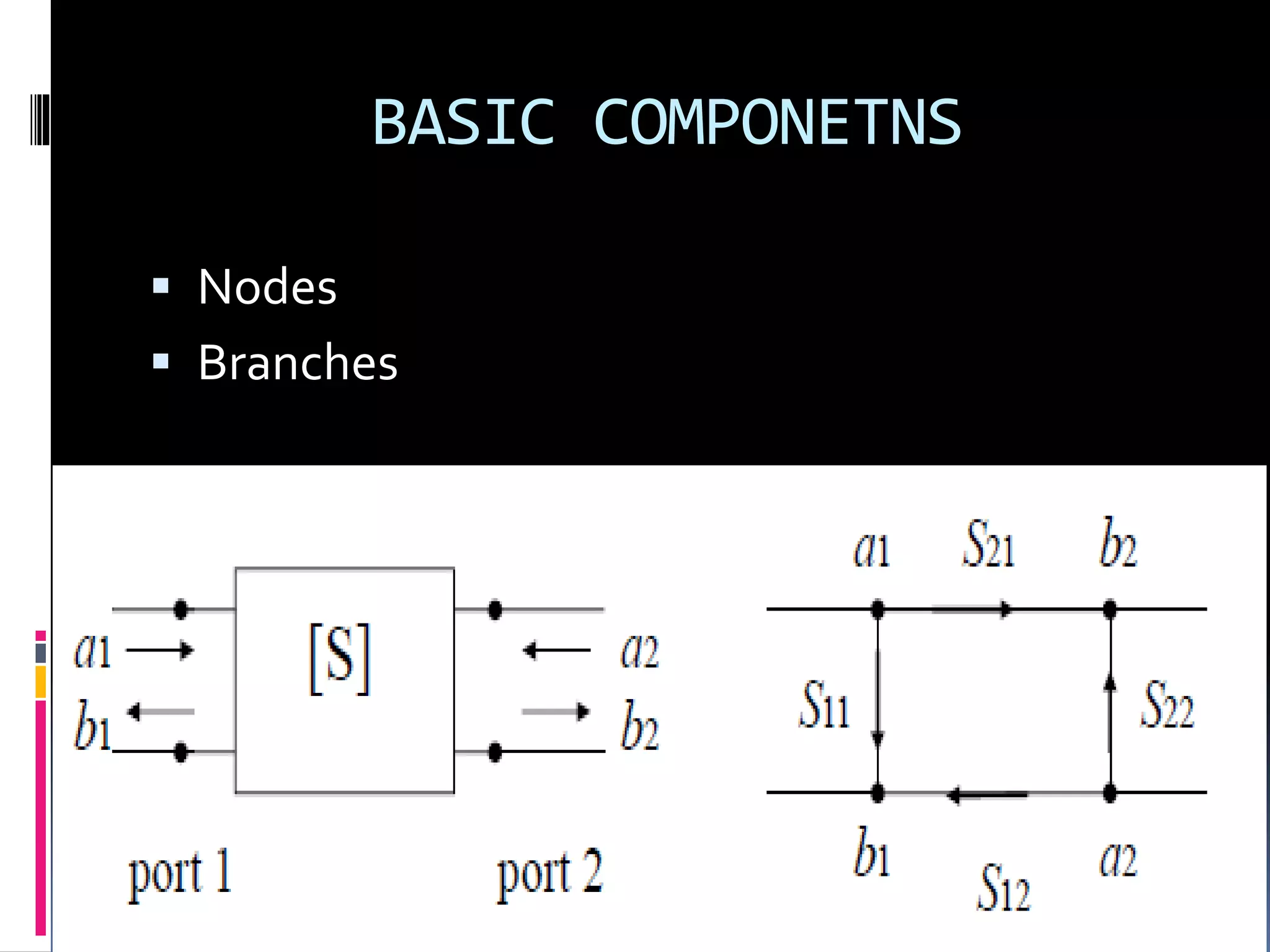
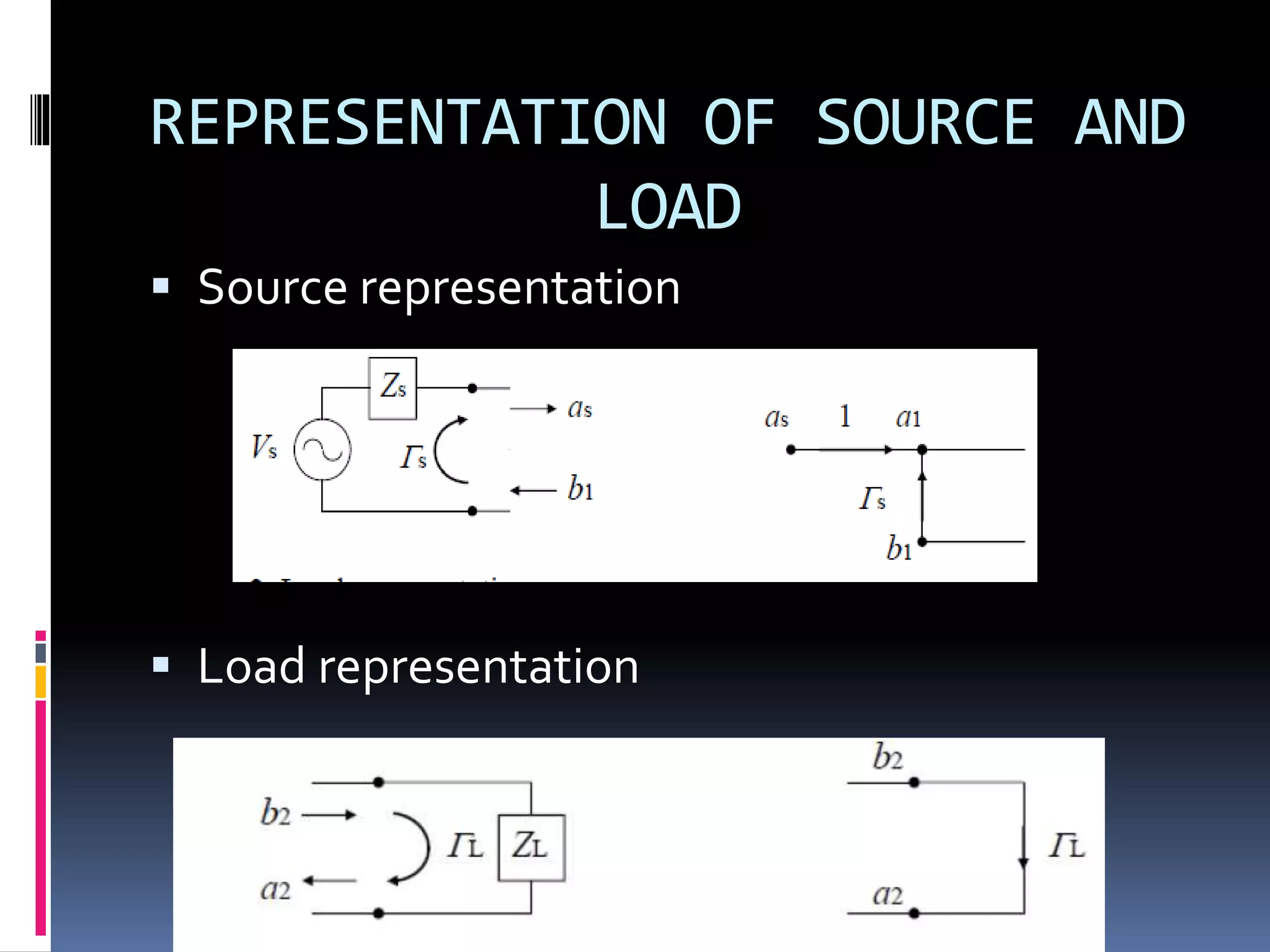

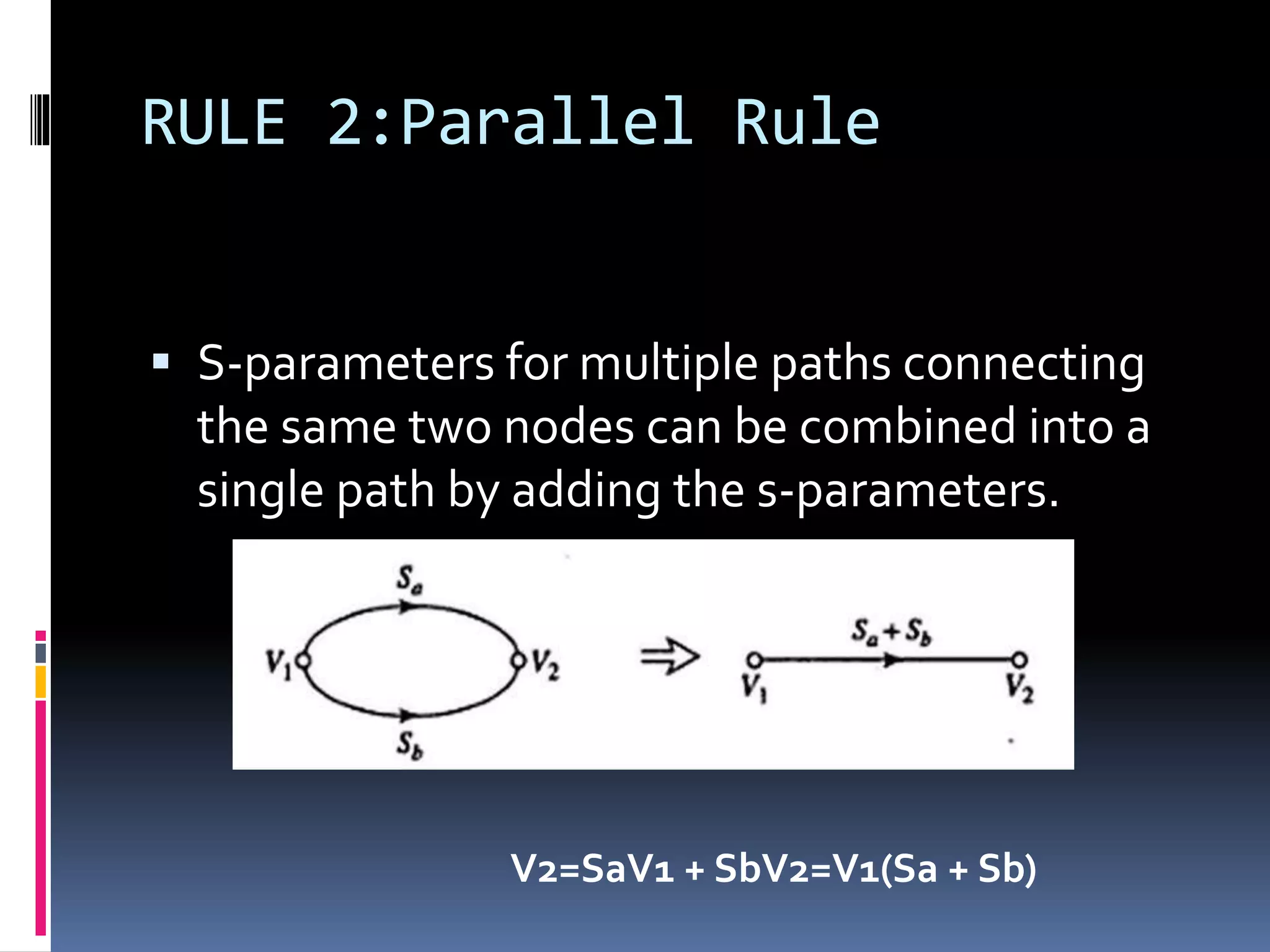

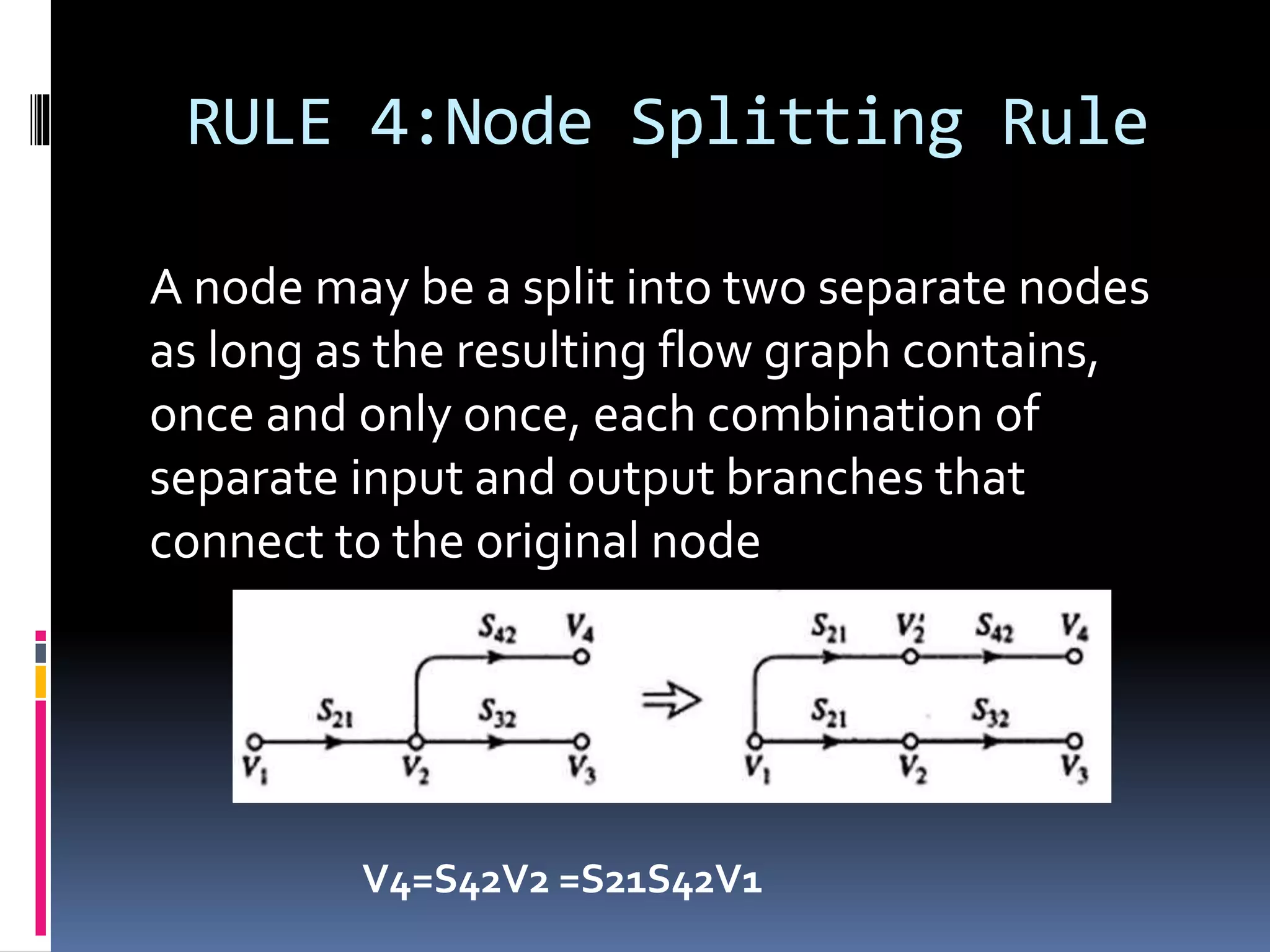
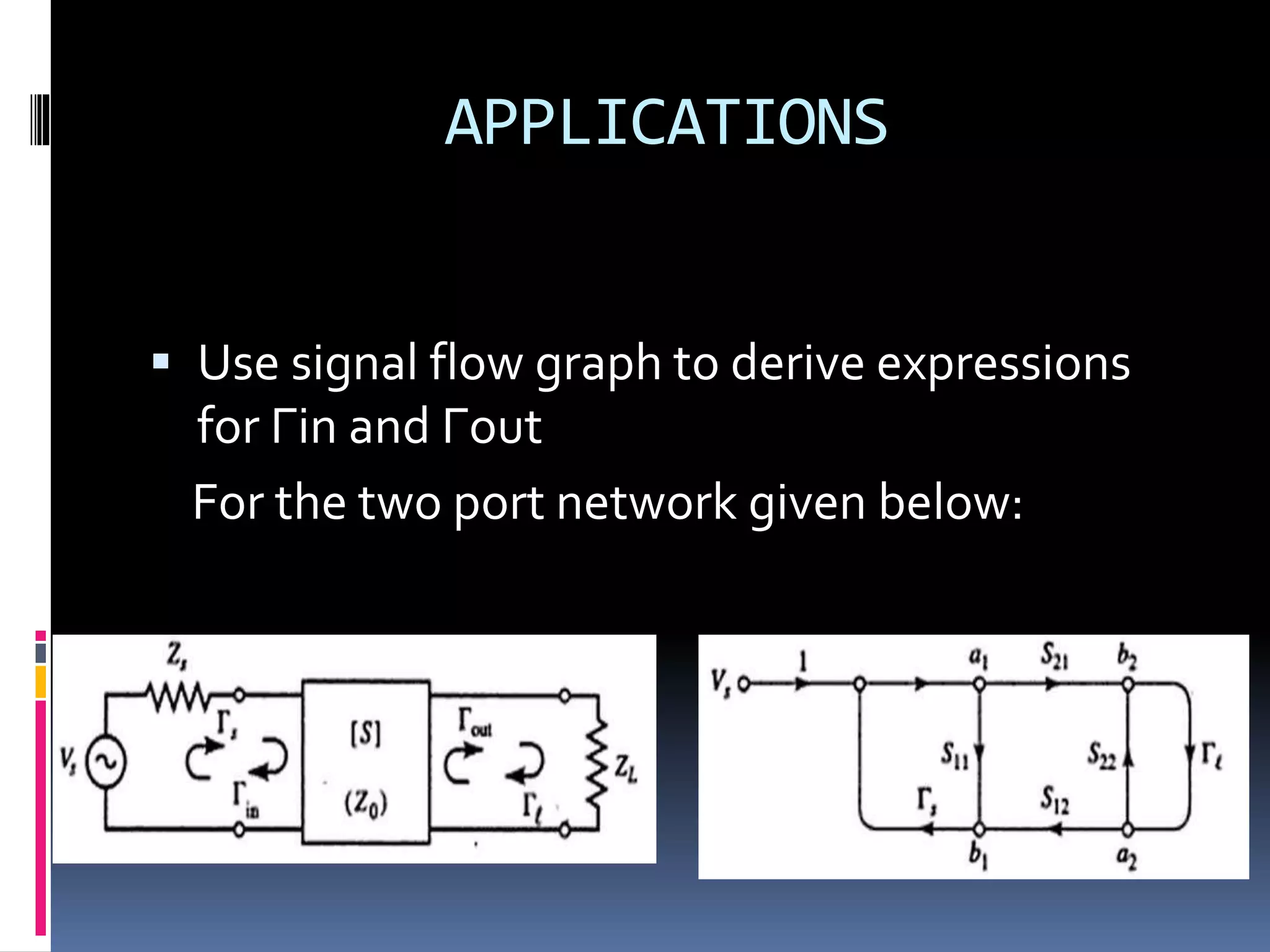
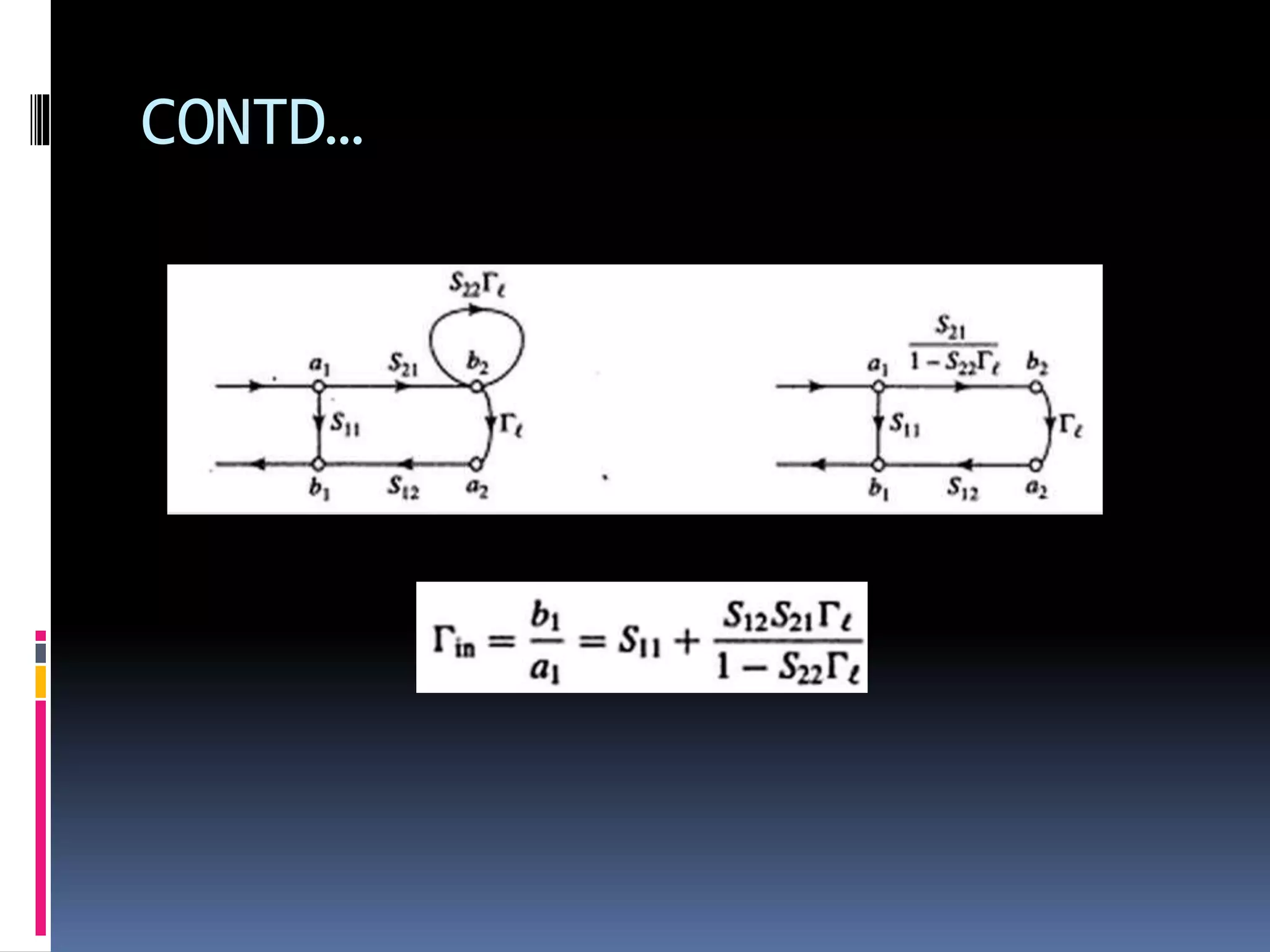
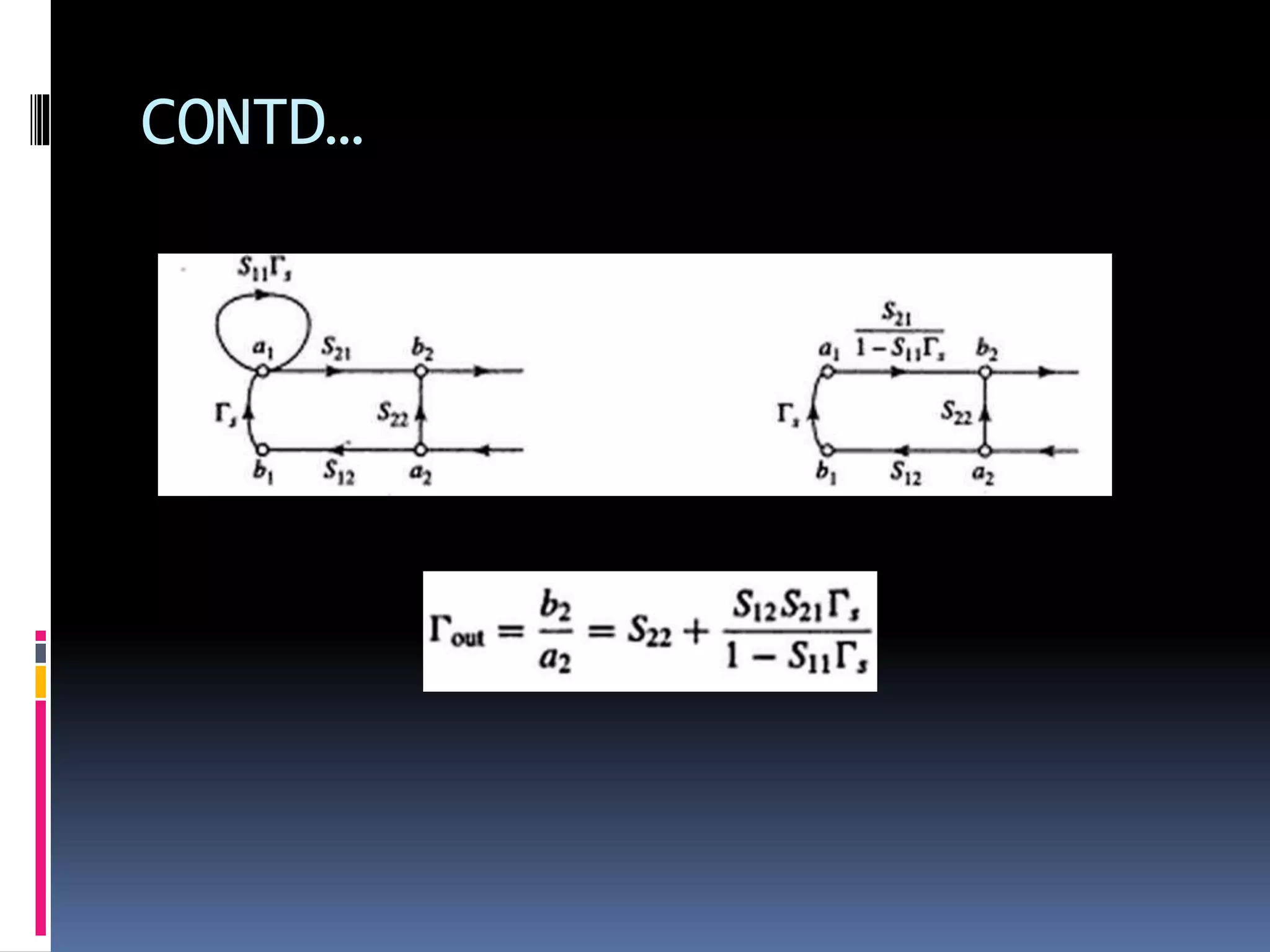


This document discusses signal flow graphs (SFG), which are a graphical technique used to analyze microwave networks in terms of reflected and transmitted waves. It introduces the basic components of SFGs, including nodes and branches, and how sources and loads are represented. The document outlines four rules for constructing and manipulating SFGs: the series rule, parallel rule, recursive rule, and node splitting rule. It provides examples of applying each rule. The document concludes by stating that SFGs can be used to derive expressions for input and output reflection coefficients Γin and Γout of microwave networks.













