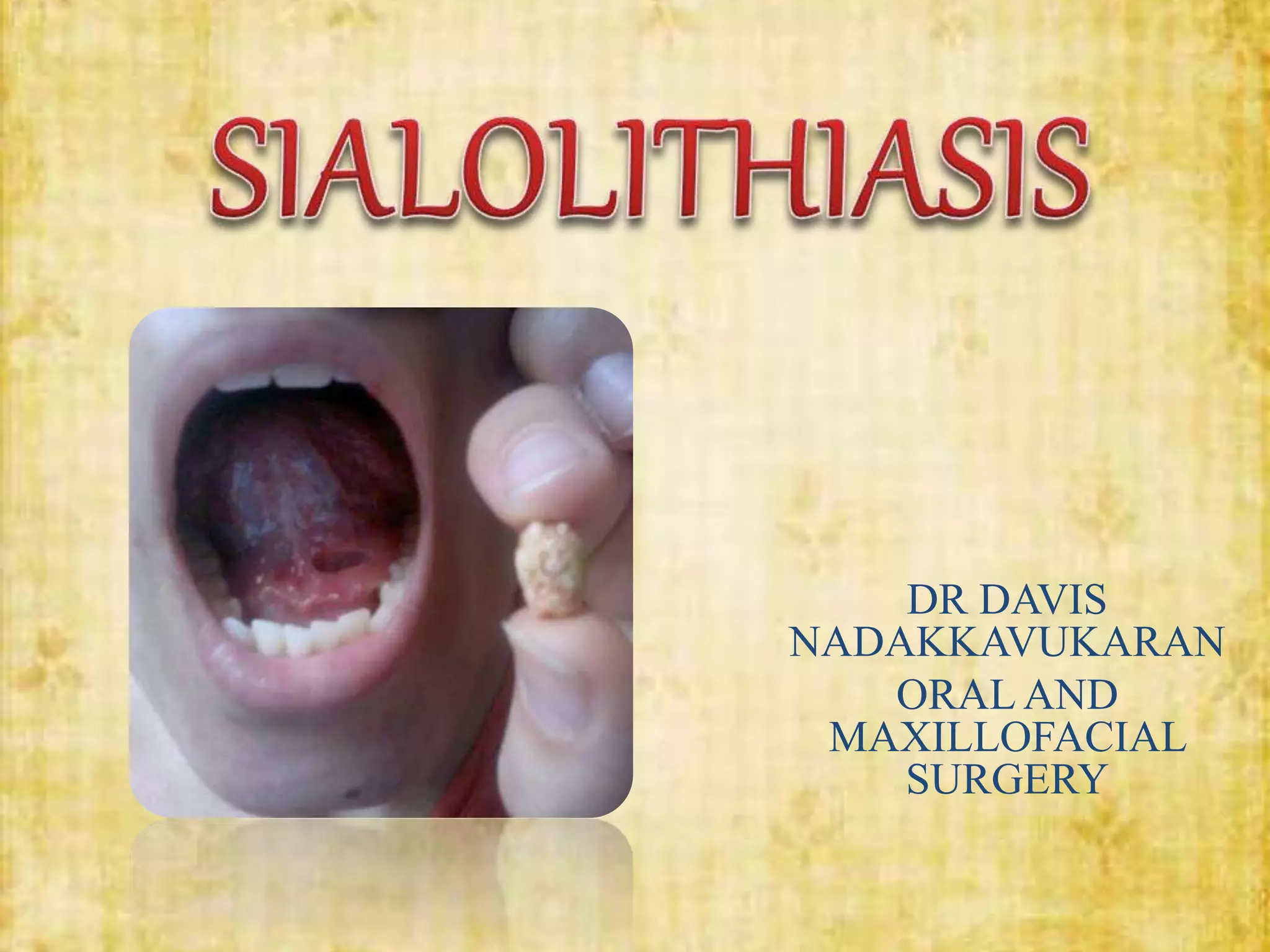
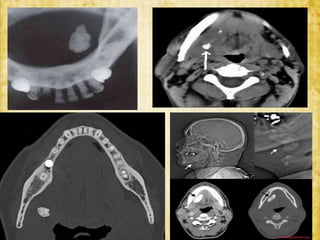
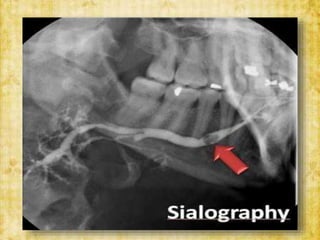
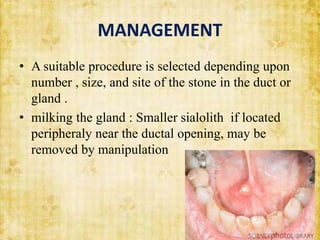
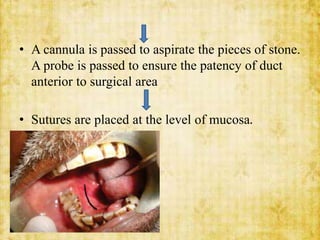
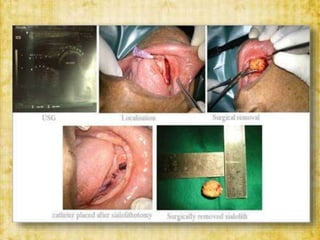
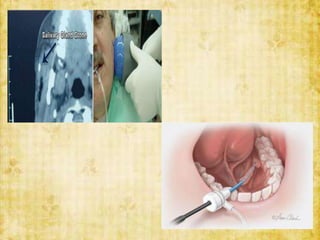
This document discusses sialolithiasis, which is the formation of salivary stones in the salivary ducts or glands. Sialoliths are calcified masses that form from the crystallization of salivary minerals. Sialolithiasis most commonly occurs in the submandibular gland due to anatomical factors. Clinically, patients experience pain and swelling during or after eating. Investigations like radiographs and sialography can detect sialoliths. Larger stones may be removed surgically through the duct or gland. Complications include inflammation, duct dilation, and gland atrophy if left untreated.