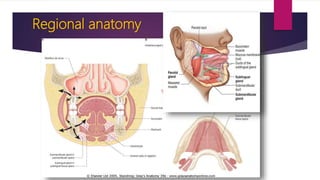
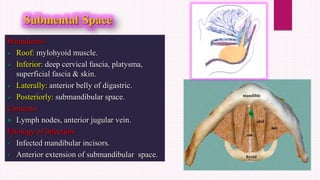
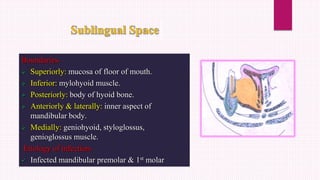
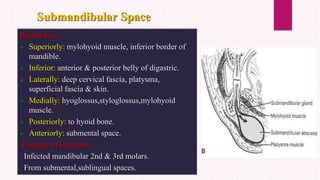
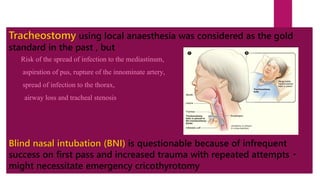
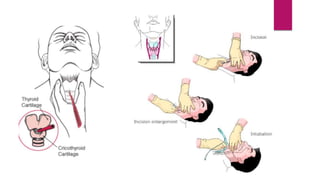
Ludwig's angina is an acute, potentially life-threatening infection of the submandibular space that causes severe swelling and difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing. It usually stems from dental infections. Clinical features include bilateral swelling of the submandibular region, elevated tongue, and difficulty speaking or swallowing. Management involves securing the airway through tracheostomy or intubation, administering IV antibiotics, and incising and draining any abscesses through bilateral submandibular and submental incisions. Early diagnosis, antibiotic treatment, and surgical drainage are crucial for successful treatment.