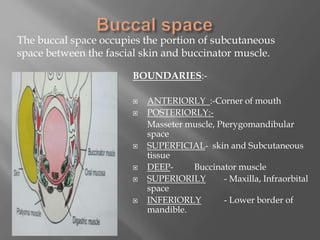
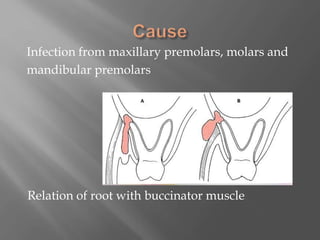
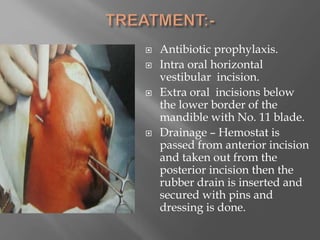
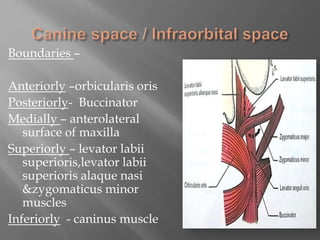
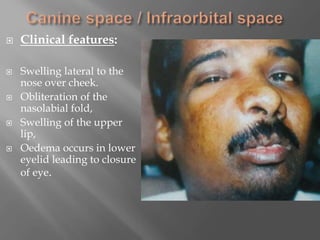
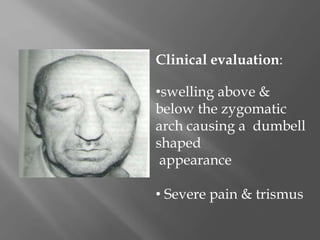
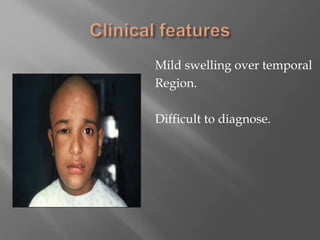
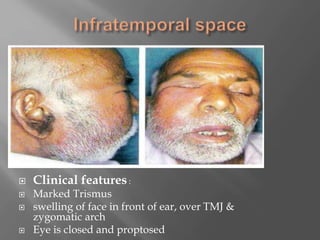
Space infections of the head and neck are common in oral and maxillofacial practice. While most infections can be managed successfully with minimal complications, some can cause serious morbidity or death depending on the virulence of microorganisms and host resistance. Bacterial infections have the potential to spread beyond the bony confines of jaw bones into surrounding soft tissues. It is important for oral and maxillofacial surgeons to understand the anatomy of fascial spaces and spread of infection to properly manage infections and prevent complications.