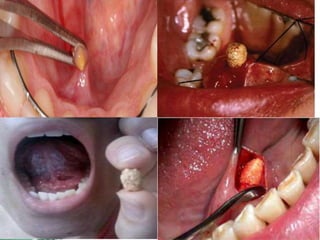
Sialolithiasis is the presence of calculi or stones in the salivary glands or ducts, which typically form due to stagnation of saliva rich in calcium. Risk factors include medications like diuretics, dehydration, gout, smoking, and chronic periodontal disease. Clinical features range from being asymptomatic to intermittent facial swelling associated with eating that can be painful or painless. Diagnosis involves ultrasound or radiographs of the affected gland. Most cases are managed conservatively with hydration and sialagogues. If infected, antibiotics may be used. Definitive management includes interventional radiology procedures to extract stones or surgery to remove difficult stones or the entire gland if symptoms persist chron