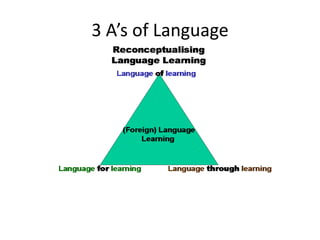
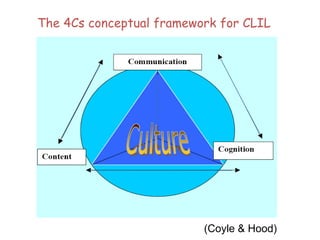
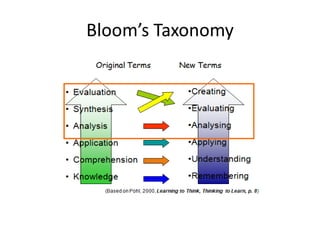
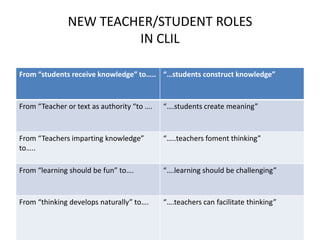
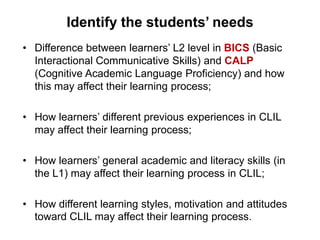
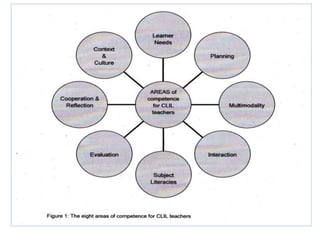
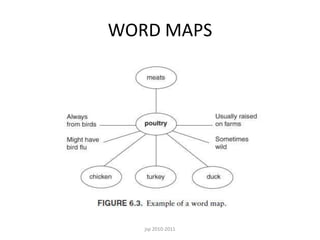
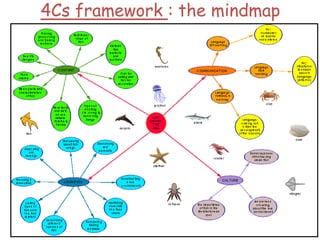
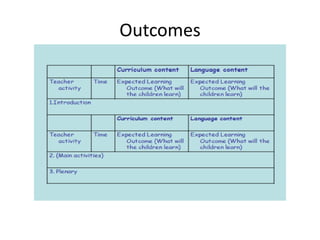
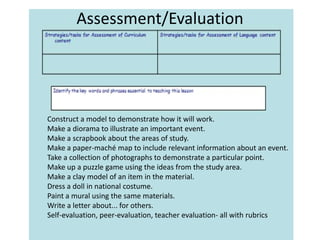
This document provides an overview of Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL). It defines CLIL as a dual-focused educational approach where an additional language is used for teaching content and language simultaneously. It discusses key CLIL concepts like integration of content and language, using language to learn new content and develop thinking skills. It also covers frameworks like the 4Cs, Bloom's Taxonomy, Cummins' Matrix. It outlines new roles for teachers and students in CLIL with a focus on facilitating thinking rather than imparting knowledge. Elements of planning, interaction, scaffolding, assessment and cooperation among teachers are also summarized.