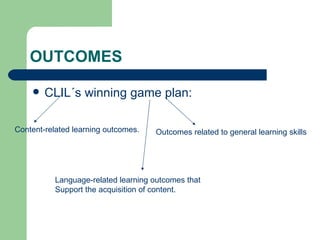
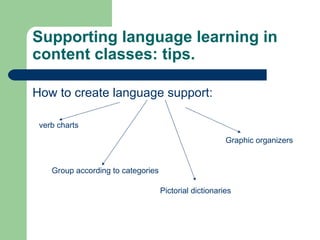
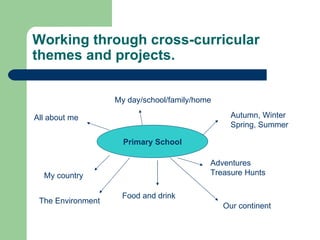
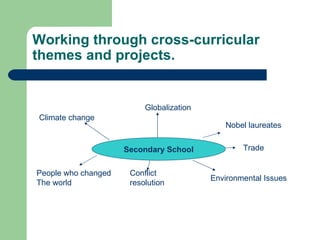
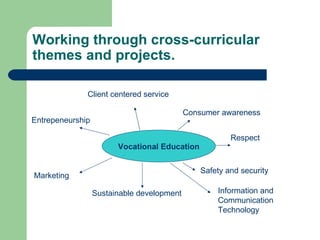
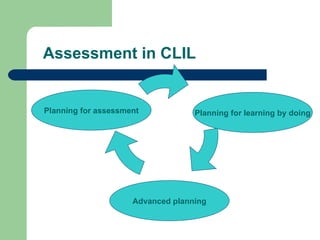
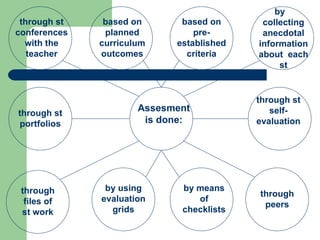
The document discusses key concepts in Content and Language Integrated Learning (CLIL), including learning outcomes, language support strategies, assessment approaches, and cross-curricular themes. It outlines that CLIL aims to support both content-related and language-related learning outcomes. It provides tips for language support, such as using repetition, modeling language, and creating opportunities for communication. Assessment in CLIL evaluates achievement of content, language and learning skills goals using various methods like student conferences, portfolios, and self-evaluation. Cross-curricular themes are suggested to create connections across subjects and engage students.