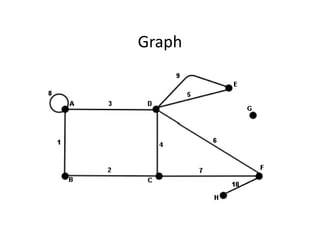
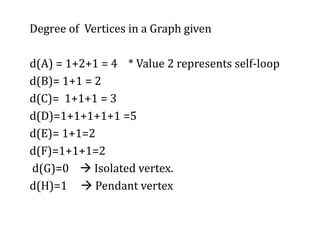
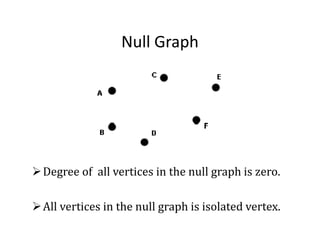
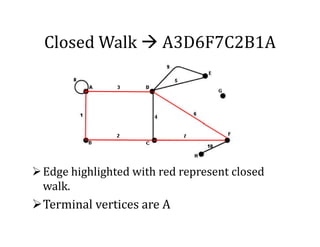
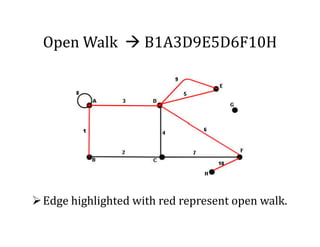
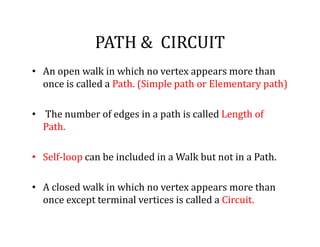
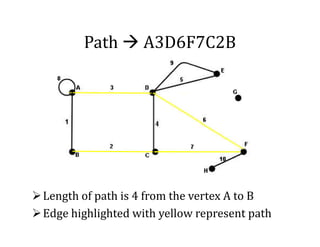
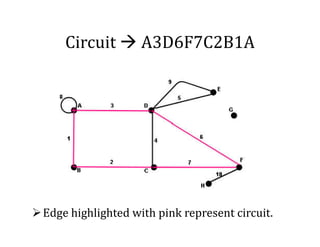
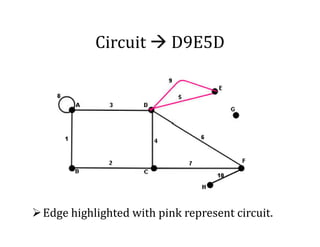
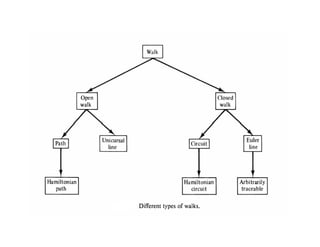
This document provides an introduction to graph theory, detailing the definitions and properties of graphs, including vertices, edges, and concepts like walks, paths, and circuits. It explains various terms such as self-loops, parallel edges, isolated vertices, and the degrees of vertices, along with examples of each. Additionally, the document addresses open and closed walks, as well as the distinctions between paths and circuits.