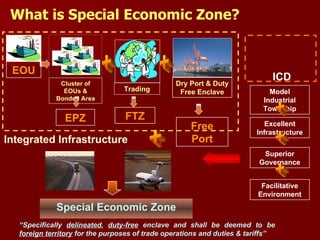
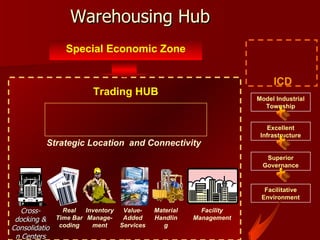
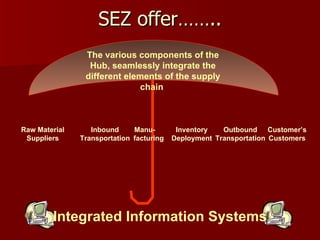
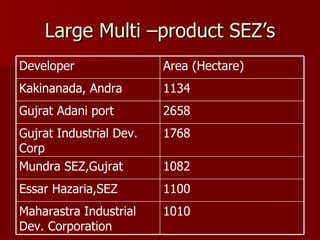
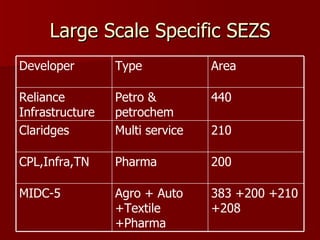
The document discusses Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India. It provides background on Export Processing Zones (EPZs) and Free Trade Zones (FTZs), which SEZs aim to improve upon. SEZs are delineated duty-free enclaves intended to promote exports by providing world-class infrastructure and business-friendly regulations. Several large multi-product and sector-specific SEZs have been approved or proposed across India with the goal of attracting investment and boosting exports.