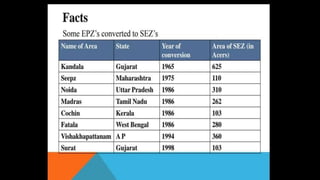
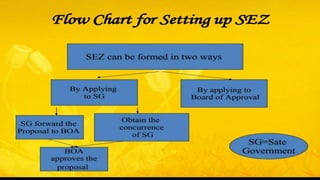
The document discusses Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India. It defines an SEZ as a specifically delineated duty free enclave within a country's territory that is treated as a foreign area for trade operations and duties. SEZs aim to attract businesses through tax incentives and reduced regulations. India first experimented with Export Processing Zones in 1965 and established its first SEZ policy in 2000 to promote exports and foreign investment through world-class infrastructure and a stable fiscal regime in dedicated industrial zones. The objectives of SEZs are to develop infrastructure, increase employment, promote international trade and attract foreign investment to drive economic growth. Businesses in SEZs receive incentives like duty exemptions, tax holidays and external borrowing