1. Money supply in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India through monetary policy to achieve objectives like price stability, full employment, and economic growth.
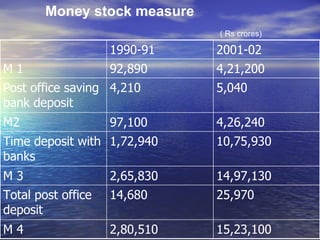
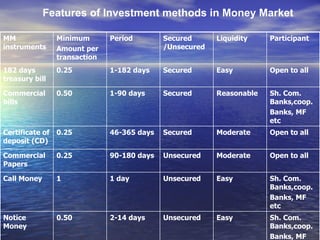
2. There is no single measure of money supply - it is measured using aggregates M1, M2, M3, and M4 which include currency in circulation and various types of bank deposits.
3. The growth in money supply must be higher than the growth in real national income to accommodate demand for money from income growth and a shrinking non-monetized sector of the economy.